Chapter 1: Basic Concepts in Chemical Bonding and Organic Molecules
Answers to Chapter 1 Practice Questions
1.1
Number of valence electrons:
B: 3 valence electrons
N: 5 valence electrons
O: 6 valence electrons
Cl: 7 valence electrons
Mg: 2 valence electrons
1.2
- Identify whether the following bond is “polar” or “non-polar”.
C-C: non-polar C-H: non-polar (very close electronegativity for C and H)
B-F: polar O-O: non-polar C=N: polar
- Rank the following bonds in the order of increasing bonding polarity: C—S, C—O, C—F (referring to the trend of EN, no need to use the exact EN values).
bonding polarity: C—S < C—O < C—F
1.3
Draw the Lewis structure of an N2 molecule: ![]()
1.4
Why is the following structure is not the best way to show the Lewis structure of CO2?
![]()
Because the formal charges are not minimized in the above structure. The formal charge in the best Lewis structure of CO2 are all zero, and the best Lewis structure of CO2 is shown here:
![]()
1.5
Draw all the equivalent resonance structures for the following species. Include any non-zero formal charges in the structures.
- O3 molecule
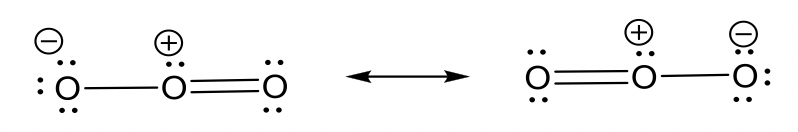
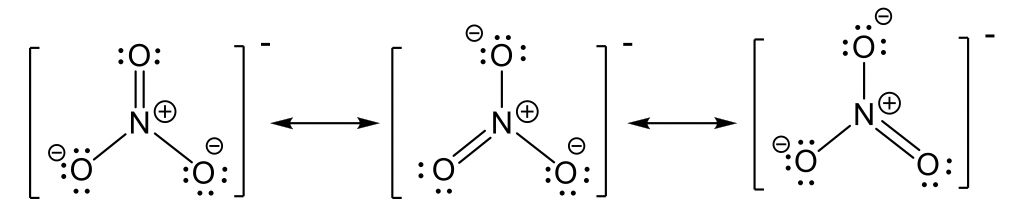
- nitrate anion NO3–
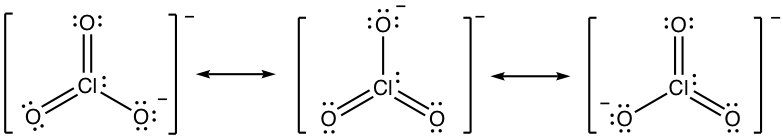
- chlorate anion ClO3–
1.6
Draw all the resonance structures for the azide anion, N3–, and indicate the most stable one.
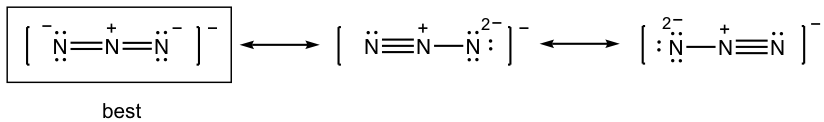
1.7
Draw a new resonance structure and compare the relative stability; show the arrows in the original structure.
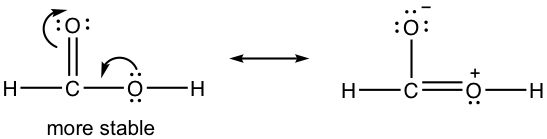
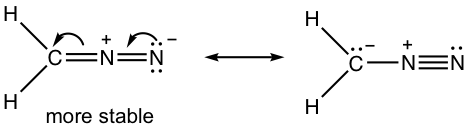
1.8
- What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in a H2O molecule?

- What is the hybridization of the xenon atom in an XeF4 molecule, and what is the shape of the whole molecule?


