Chapter 9: Free Radical Substitution Reaction of Alkanes
9.1 Homolytic and Heterolytic Cleavage
For the reactions we learned about so far, bond breaking occurs when one part of the bond takes both electrons (the electron pair) of the bond away. For example, for an SN1 reaction, the leaving group Br leaves with the electron pair to form Br– and carbocation intermediate.
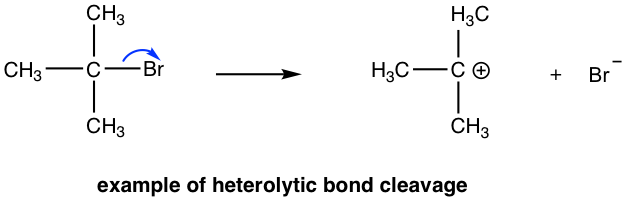
This process is called heterolytic bond cleavage, and the σ bond breaks heterolytically. As before, an arrow with double-barbs is used to show heterolytic cleavage, which is the transfer of the electron pair specifically:
There is another type of bond-breaking process, in which each part of the σ bond takes one electron away, as shown below:
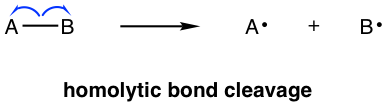 This is called homolytic cleavage or homolysis. The electron pair separates evenly to each part, and as a result, both products contain a single electron. The species that contains one or more single electrons is called a radical (or free radical). Radicals are produced from homolytic cleavage. The arrow with a sing-barb (like the shape of a fishhook) is used to show homolytic cleavage, which is single electron transfer specifically:
This is called homolytic cleavage or homolysis. The electron pair separates evenly to each part, and as a result, both products contain a single electron. The species that contains one or more single electrons is called a radical (or free radical). Radicals are produced from homolytic cleavage. The arrow with a sing-barb (like the shape of a fishhook) is used to show homolytic cleavage, which is single electron transfer specifically:
Homolysis occurs mainly for non-polar bonds, and heat or light (Δ is the symbol for heat; hν is used to show light) is needed to provide enough energy to initiate the process. Two examples of radicals generated from homolysis are shown below.

A radical is another highly reactive reaction intermediate, because of the lack of an octet. The substitution reaction we will learn about in this chapter involves the radical intermediate.

