Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Organic Structures
2.2 Nomenclature of Alkanes
As it has been shown that the number of constitutional isomers increases dramatically as the number of carbons increases, it is impossible to give each structure its own common name, like isobutane. As a result, a systematic method with certain rules is necessary when it comes to naming organic compounds. In this book, we will learn about IUPAC nomenclature; it is also the systematic nomenclature that has been widely adopted internationally. IUPAC nomenclature was initially designed by a commission for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in 1892, and it has been continually revised by the commission since then.
IUPAC NOMENCLATURE of ALKANES
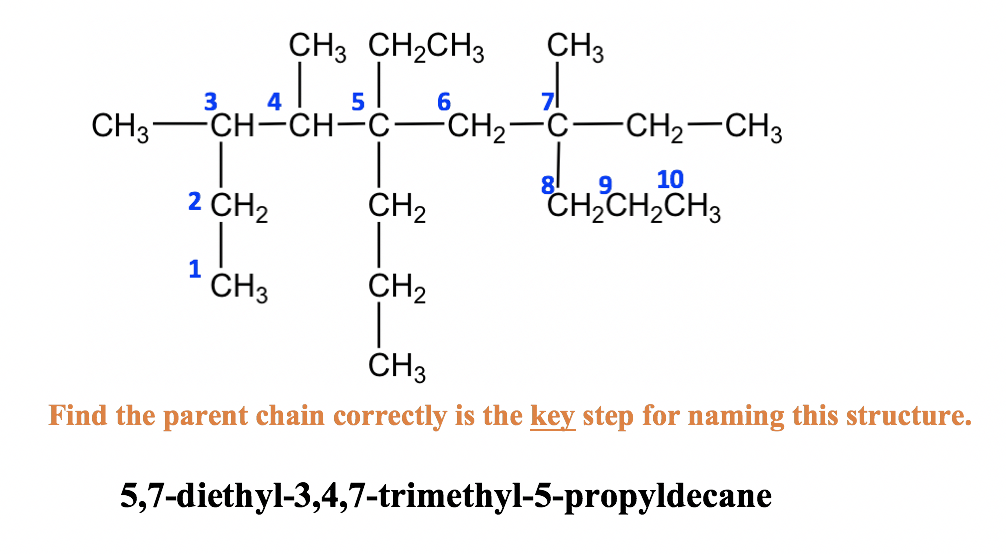
- Identify the longest continuous carbon chain as the parent chain. This chain determines the parent name (or last name) of the alkane.
- If there are two choices of the same length, then the parent chain is the longest chain with the greatest number of “branches”. The term substituent will be used from now on as the official name for “branch”.
- Number the chain beginning at the end that is closest to any substituents, thus ensuring the lowest possible numbers for the positions of substituents.
- Use these numbers to designate the location of the substituent groups, whose names are obtained by changing the “-ane” suffix to “-yl“.
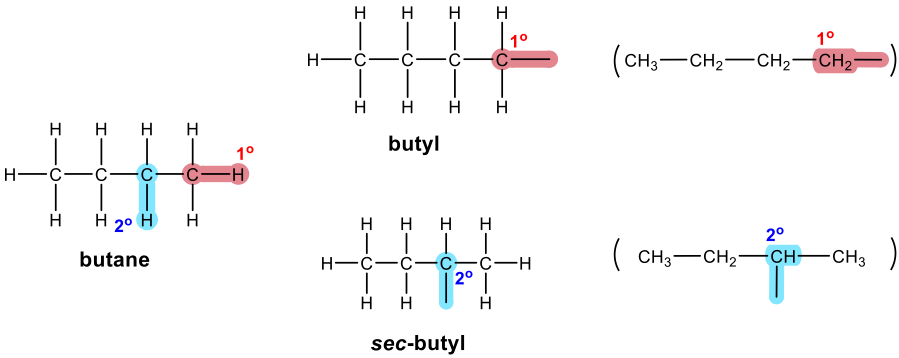
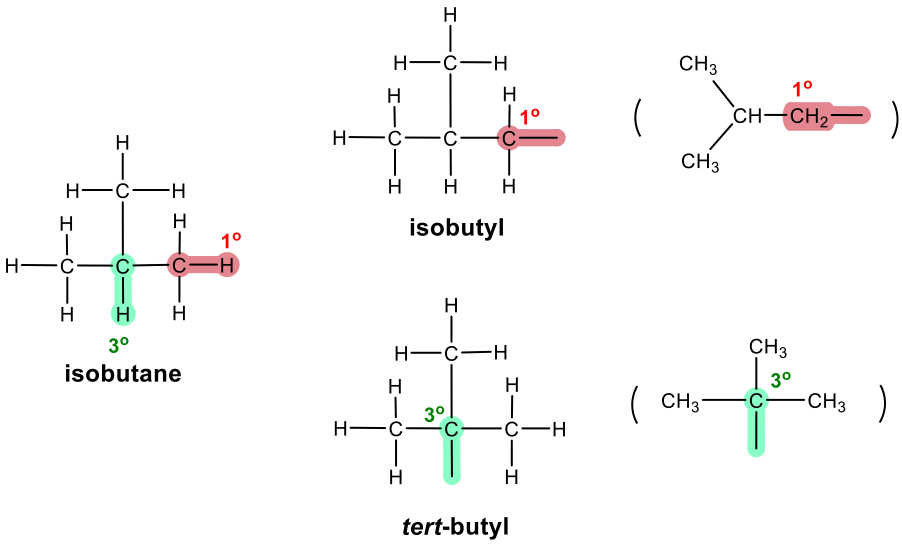
The substituents derived from alkane are also called alkyl groups.
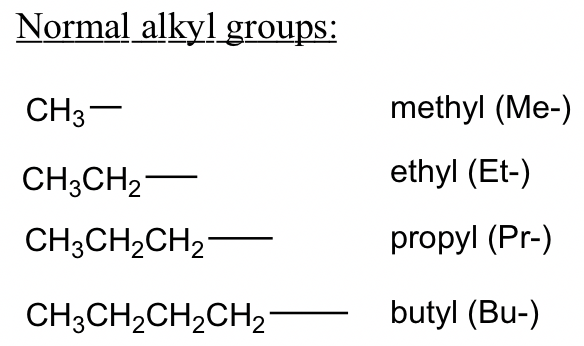
- If an alkyl substituent group appears more than once, use the prefixes di, tri, tetra, penta, and hexa (meaning 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 respectively) for each type of alkyl group.
- List the substituent groups alphabetically (use the substituent group name from step 3, ignore the prefixes from 4, but include “iso” and “cyclo”).
- Write the name as a single word. Numbers are separated from letters by “-“; numbers are separated by “,”.
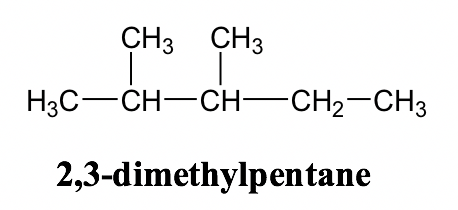
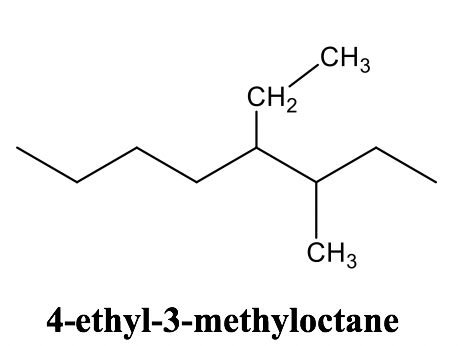
Alkane Naming Examples:
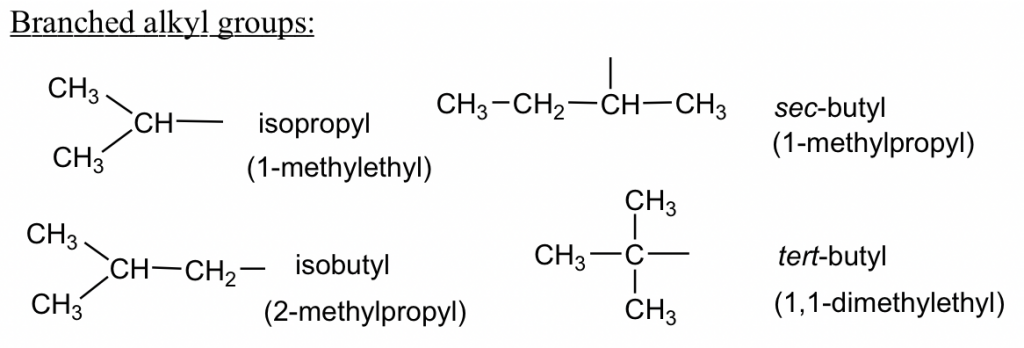
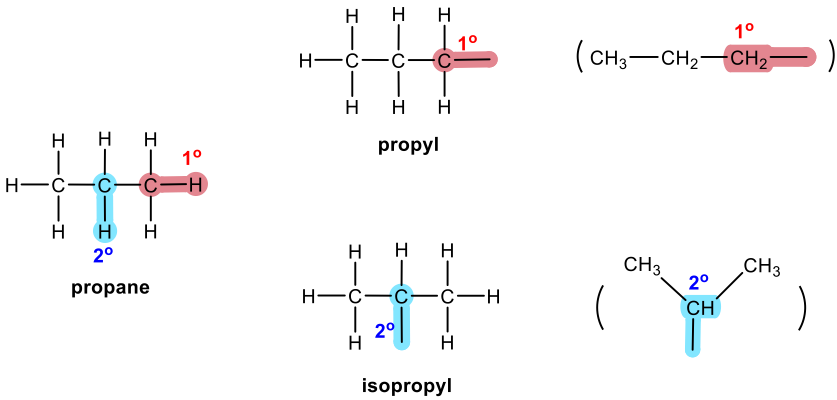
Three-carbon branched alkyl groups
IUPAC name of branched alkyl groups
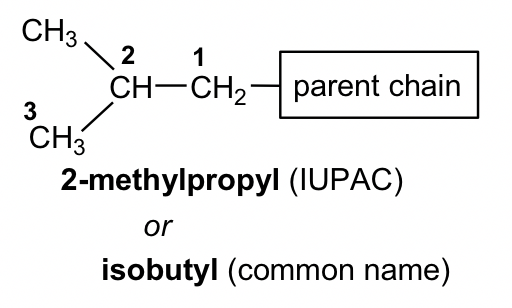
The branched alkyl groups can also be named by IUPAC rules. To do that, they are treated as if they were a compound. Begin numbering at the point of attachment to the parent chain, and the same number of branches as before to avoid confusion. The complex substituent name is put in parentheses when the name of the complete molecule is written.
For the example of isobutyl below, the part that connects directly to the parent chain has 3 carbons, so it is “propyl”. There is another CH3 on the 2nd carbon of propyl; therefore, the whole group is called “2-methylpropyl”.
Naming of Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes are alkanes that contain a ring(s) as part of the structure. For a cycloalkane that contains one ring, there are two fewer hydrogens than the non-cyclic alkane, so the general formula of cycloalkanes with one ring is CnH2n.
IUPAC NOMENCLATURE of CYCLOALKANES
- The parent name is “cycloalkane”.
- Number the ring to provide the lowest possible numbering sequence (when two such sequences are possible, cite substituents in alphabetical order, and the No. 1 position is given to the first cited substituent).
Example:
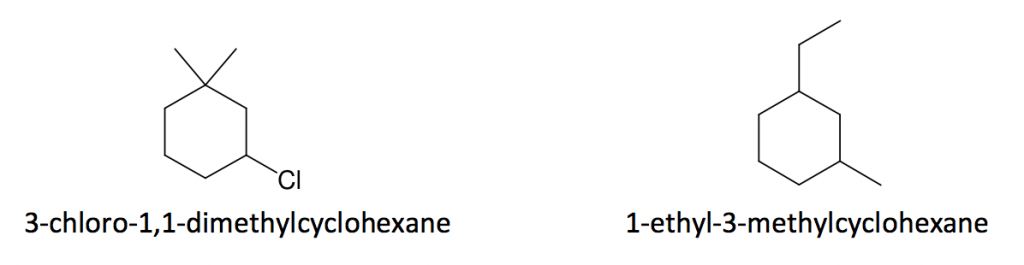
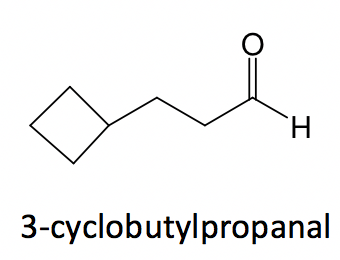
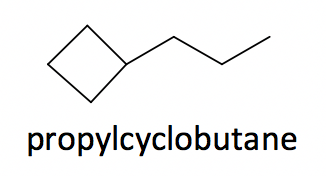
3. When both the ring and chain are included in the structure, compare the number of carbons in the ring vs the chain and select the one with more carbons as the parent structure; the other is treated as a substituent.
Example:
4. When higher-priority functional groups are present (more in section 2.2), parent structure will contain that functional group.
Example: