Chapter 10: Alkenes and Alkynes
10.6 Two Other Hydration Reactions of Alkenes
As we learned in section 10.2.2, the acid-catalyzed hydration (addition of water) to alkene produces alcohol that follows Markovnikov’s regioselectivity. Here, we will investigate two other methods for the hydration of alkene via different reaction conditions and mechanisms and produce either Markovnikov or anti-Markovnikov alcohol products, respectively.
10.6.1 Oxymercuration-Demercuration of Alkenes
Oxymercuration-demercuration is a two-step procedure, as shown explicitly below:
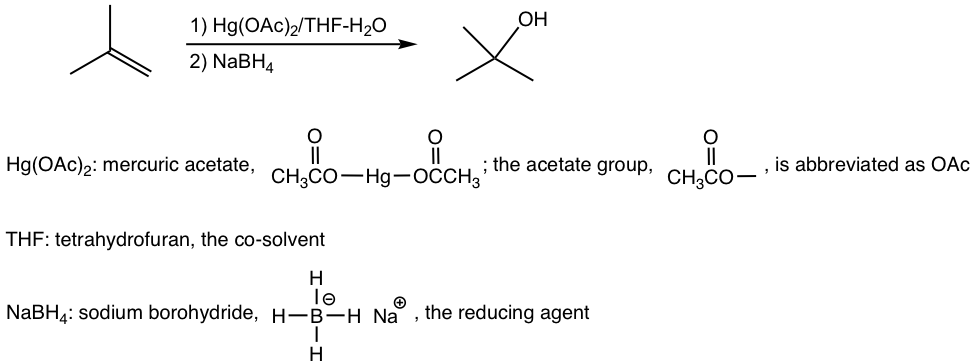
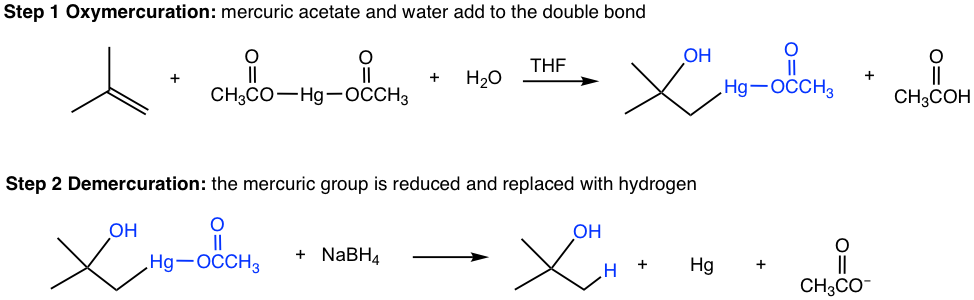
The mechanism in the oxymercuration step involves mercury acting as a reagent attacking the alkene double bond to form a cyclic mercurinium ion intermediate. Because no carbocation intermediate is involved, rearrangements are not observed in a such reaction. Then, a water molecule attacks the most substituted carbon to open the mercurium ion bridge followed by proton transfer to a solvent water molecule. For the same reasoning that the water molecule attacks the more substituted carbon of the cyclic halonium ion in a halohydrin formation (section 10.2.4), the water molecule in this mechanism also attacks the more substituted carbon preferentially, as the partial positive charge is better accommodated on a tertiary carbon than on a primary carbon (if the attack occurs on the other carbon).

The organomercury intermediate is then reduced by sodium borohydride. The mechanism for this final step is beyond the scope of our discussions here. Notice that the overall oxymercuration-demercuration mechanism follows Markovnikov’s rule with the OH group attached to the most substituted carbon, and the hydrogen atom adds to the less substituted carbon.
10.6.2 Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkenes
Hydroboration-oxidation is another method for converting alkene to alcohol; however, in anti-Markovnikov regioselectivity, OH is bonded to the carbon with a greater number of hydrogens, and the hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbon with fewer hydrogens.
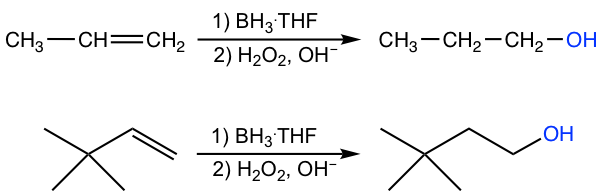
The overall reaction is also a two-step process:
- The first step is hydroboration, which is the addition of boron atoms and hydrogen atoms to the alkene.
- The second step is oxidation and hydrolysis of the alkylborane formed in step 1 to produce alcohol.
The borane reagent used in the first step is usually available as the solution containing a BH3·THF complex. Borane, BH3, is an electron-deficient species because the boron atom has an incomplete octet with only six electrons. When BH3 is introduced to THF, they react to form a Lewis acid-Lewis base adduct (Chapter 3), which is more stable and relatively easy to handle and store. The solution containing BH3·THF is still sensitive and must be used in an inert atmosphere (nitrogen or argon) and with care.
Because of the incomplete octet of the boron atom in BH3, it is a good electrophile that reacts with alkene. The mechanism of the hydroboration step is illustrated below with propene as the example.
Mechanism of Hydroboration
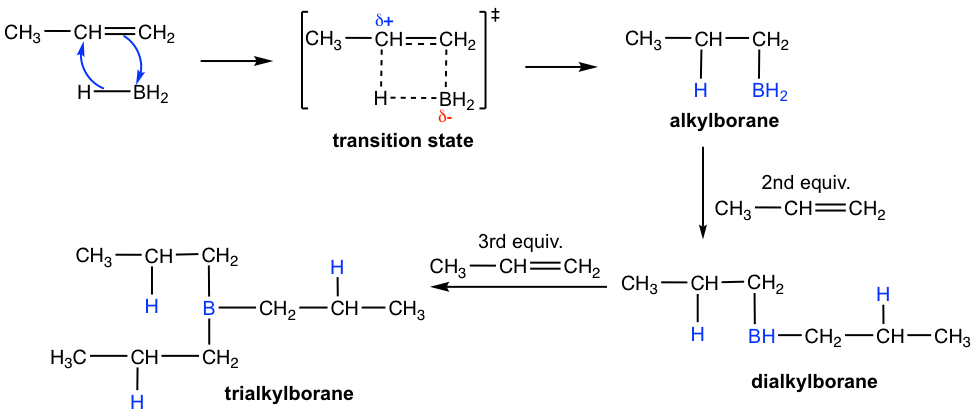
When a terminal alkene, for example, propene, is treated with BH3·THF, the BH3 molecule adds successively to the C=C double bond of three alkene molecules to form a trialkylborane. In each additional step, the boron atom becomes attached to the less substituted double bond carbon, and a hydrogen atom is transferred from the BH3 to the more substituted carbon. In the second step (oxidation and hydrolysis) of the whole process, the borane is oxidized and hydrolyzed to the OH group. So, the regioselectivity of the hydroboration step defines the anti-Markovnikov regioselectivity of the overall reaction.
Such regioselectivity of the hydroboration step can be explained by both electronic and steric effects. In terms of the steric factor, the boron-containing group is more bulky than the hydrogen atom, so they can approach the less substituted carbon more easily. The electronic effect lies in the transition state structure for the formation of alkylborane. As shown above, the π electrons from the double bond are donated to the π orbital of boron and a four-atom ring cyclic transition state is approached. In the transition state, electrons shift in the direction of the boron atom and away from the carbon that is not connected to the boron. This makes the carbon not connected to the boron bear a partial positive charge, which is better accommodated on the more substituted carbon. As a result, the electronic effect also favors the addition of boron on the less substituted carbon.
Stereochemistry of Hydroboration
Hydroboration-oxidation takes place with syn stereochemistry, in which the OH group and the hydrogen atom add to the same side of the double bond, as shown in the following example.
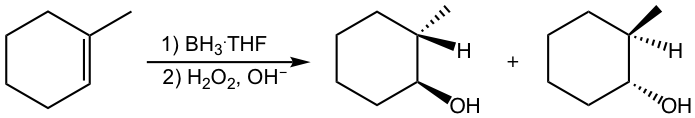
This can be explained by the mechanism of the hydroboration step. The four-membered ring transition state requires that the boron atom and the hydrogen atom approach the same surface of the alkene double bond so they are added in the syn position to the double bond. Since the boron part is converted to the OH group in the second step, it results in the syn addition of OH and H in the product.
Oxidation and Hydrolysis of trialkylboranes
When the hydroboration reaction is over, the trialkylboranes are usually not isolated; they are oxidized and hydrolyzed with the addition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in a basic aqueous solution. The mechanism for the oxidation and hydrolysis of trialkylboranes is complicated and could be an optional topic, but the net result is that the boron initially bonded on the carbon is replaced by the hydroxy OH group.
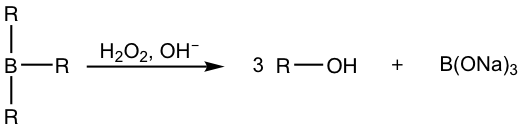
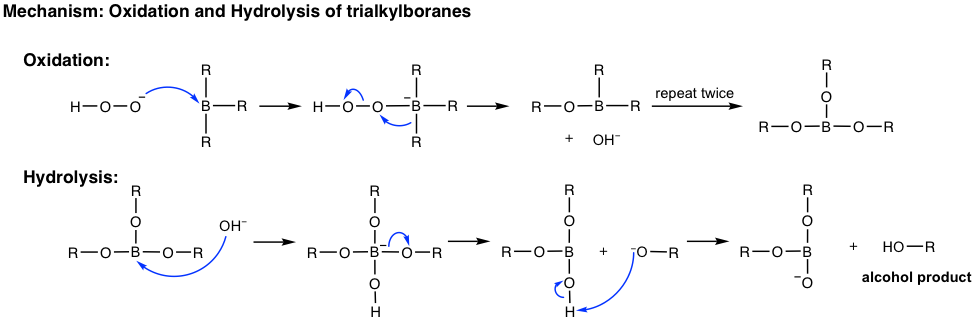
Summary: Hydration Methods of Alkene
Overall, there are three methods for converting alkene to alcohol via addition: acid-catalyzed hydration, oxymercuration-demercuration, and hydroboration-oxidation, as summarized in Table 10.1. Each method has its benefits and drawbacks. The proper method can be chosen based on the need.
| Acid-catalyzed hydration | Oxymercuration-demercuration | Hydroboration-oxidation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction Conditions | cat. H+/H2O |
1)Hg(OAc)2/THF·H2O
2)NaBH4
|
1) BH3·THF
2) NaBH4
|
| Regioselectivity | Markovnikov | Markovnikov | Anti-Markovnikov |
| Stereochemistry | Not controlled | Not controlled | syn-addition |
| Rearrangement | Yes | No | No |
Table 10.1 Summary of methods for conversion of alkene to alcohol

