Chapter 1: Basic Concepts in Chemical Bonding and Organic Molecules
1.5 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
The Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory helps us understand and predict the geometry (shape) of molecules or ions. The theory states that:
- Electron pairs repel each other whether they are in chemical bonds or lone pairs.
- Valence electron pairs are oriented to be as far apart as possible to minimize repulsions.
Based on this theory, depending on the number of electron pairs (both bonding pairs and lone pairs) around the central atom, a certain shape is adopted to minimize the repulsion between electron pairs, as summarized in Table 1.2 below:
|
Total number of electron groups (electron pairs) around the central atom |
Geometry (Shape) of electron groups (electron pairs) |
|---|---|
|
2 |
linear |
| 3 | trigonal planar |
| 4 | tetrahedral |
| 5 | trigonal bipyramidal |
| 6 | octahedral |
Table 1.2 Basic VSEPR Shapes
Notes:
- For VSEPR purposes, the terms “shape” and “geometry” are interchangeable; “electron pair” and “electron group” are also interchangeable.
- Multiple bonds (double or triple bonds) are regarded as one electron group for VSEPR purposes.
For species that do not have any lone pair electrons (LPs), the geometry (shape) of the species is the same as the geometry of the electron groups.
For the example of the PCl5 molecule, there are five electron groups on the central phosphorous, and they are all bonding pairs (BPs). The shape of the electron groups is trigonal bipyramidal, and the shape of the PCl5 molecule is trigonal bipyramidal as well. The trigonal bipyramidal shape can be drawn on paper using solid and dashed wedges: the three bonds that lie within the paper plane are shown as ordinary lines, the solid wedge represents a bond that points out of the paper plane, and the dashed wedge represents a bond that points behind the paper plane.
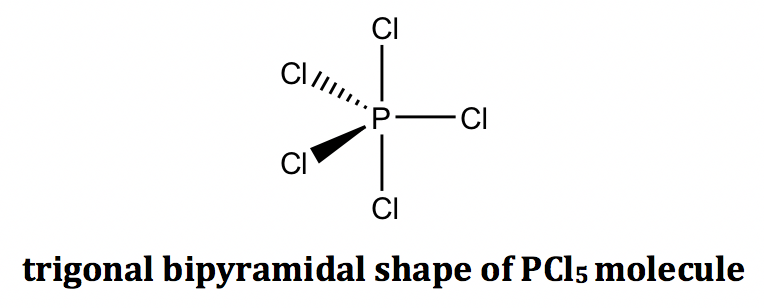
However, for the species that has lone pair electrons on the central atom, the shape of the species will be different from the shape of the electron groups. The reason is that even though the lone pairs occupy the space, there are no terminal atoms connected with the lone pairs, so the lone pairs become “invisible” for the shape of the species.
For the example of the water (H2O) molecule, the central oxygen atom has two BPs and two LPs, and the shape of all the electron groups is tetrahedral. The shape of a water molecule is bent because only the atoms are counted towards the molecular shape, not the lone pair electrons.
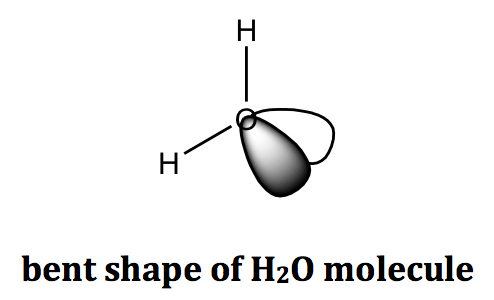
The VSEPR shapes can be highly diverse, considering the different numbers of total electron pairs together with the different numbers of lone pairs involved. The most common shapes are summarized in the following table (Table 1.3). To describe a certain shape, the specific name has to be used properly, and the bond angle information is important as well.
| Total number of e-groups | Geometry (shape) of all the electron groups | # of Bonding Pairs (BP) and Lone Pairs (LP) | Geometry (shape) of the species | Angles (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | linear | 2BP | linear | 180 |
| 3 | trigonal planar | 3BP | trigonal planar | 120 |
| 2BP, 1LP | bent | <120 | ||
| 4 | tetrahedral | 4BP | tetrahedral | 109.5 |
| 3BP, 1LP | trigonal pyramidal | <109.5 | ||
| 2BP, 2LP | bent | <109.5 | ||
| 5 | trigonal bipyramidal | 5BP | trigonal bipyramidal | 120, 90, 180 |
| 4BP, 1LP | see-saw | <120, 90, 180 | ||
| 3BP, 2LP | T-shape | 90, 180 | ||
| 2BP, 3LP | linear | 180 | ||
| 6 | octahedral | 6BP | octahedral | 90, 180 |
| 5BP, 1LP | square pyramidal | 90, 180 | ||
| 4BP, 2LP | square planar | 90, 180 |
Table 1.3 Summary of specific VSEPR shapes
The website Molecule Shapes https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/molecule-shapes/latest/molecule-shapes_en.html provides good resources for visualizing and practicing VSEPR topics.
We will see more applications of VSEPR in organic compounds in the next section.

