25 Change Management
Arley’s comments: You’ve done a thorough job here. As you mentioned, this was a big topic, and you did a great summary of different models of change management and why it’s important. You also did some good research. I think you’ve covered all of the main points and used clear headings etc. to do so. However, my biggest piece of feedback is that, while you did cite your sources, you often used a sentence from the source and then changed a few words. This sometimes makes the sentence hard to read, since different words have different connotations. It makes it hard for us to use our brand voice. In the revision, I’d like to see this section use our brand voice and more plain language. Also, make sure that you only use images that have a Creative Commons license.
Judy’s comments:
This is not an easy topic and therefore good job for taking this on and putting together information that is both credible and engaging. The main 2 things that I see missing here are: 1) the ADKAR change model – it is commonly used in HR – need to include a write up, the steps, and a link to a video (as done with the other 2 models), 2) HR’s role as a change agent (I would suggest including the roles of all key stakeholders – employees, managers, union, etc). Lastly, I am not sure about keeping the information on “Costs of Change Management” as some of this is covered under the benefit section which is more applicable to your audience.
Learning Objectives
- What is Change Management
- Principles of Change Management
- Change Management Models
- Benefits of Change Management
- When is Change Management Required & What are its Impacts
- Role of HR in Change Management
Change Management

Change management is the essence for the employee engagement (Perkins, Bart, 2018). Every employee will serve as an ambassador or advocate for the firm (Gerbec, 2017). In order to do things better, every organization will be looking at changes it can implement in the firm (Perkins, Bart, 2018). The changes must be well planned and put forward in a proper manner (Perkins, Bart, 2018). Otherwise, it would put the organization in misfortune. This is where the change management comes into picture (Gerbec, 2017).
First of all, change is something an organization carries out that has an impact on its day to day operations (MindTools, 2020). It could be digital transformation or just an up gradation of existing internal software or tool (MindTools, 2020). A clear definition is provided by Sheila Cox, where she states – ‘Organizational change management ensures that the new processes resulting from a project are actually adopted by the people who are affected.’ (Perkins, Bart, 2018).
Principles of Change Management:
Change management can be categorized into 4 categories, namely-
- Understand change – To convey the benefits of change one must understand as to why change is required and its vital objectives (MindTools, 2020). Then comprehend how will have a positive impact on the staff and affect the way they do the tasks (MindTools, 2020). The negative outcomes must be considered too, if the change is not bought in place (MindTools, 2020).
- Plan change – Changes can be rigid or flexible (MindTools, 2020). Therefore, the changes that are implemented in the organization will go through a clear thought process (MindTools, 2020).
- Implement change – As people would have been accustomed to practices; it takes a while for them to adapt to the new processes (MindTools, 2020). Therefore, role models must take over and exhibit them the new procedure (MindTools, 2020). Make sure that everyone is involved and they know what is happening. Also, training can be considered for individuals who need assistance for adaption (MindTools, 2020).
- Communicate change – The make or break component of communication is change management (MindTools, 2020). Therefore, it is critical that the changes are communicated in a clear and concise manner (MindTools, 2020). It would be great if one could link the changes with the organizations mission and vision (MindTools, 2020). This would help the employees to look at the bigger picture and would motivate them (MindTools, 2020). It is critical to have a good rapport with the stakeholders to get the support that is required for the projects (MindTools, 2020).
Change Management Models
There are a few change management models but the prominent ones are the Lewin’s change management model, Kotter’s 8 step change management model and ADKAR change management model.
Kurt Lewin’s change management model:
In the former the change process is divided into 3 key stages, namely – Unfreeze, change and refreeze and the latter provides a more inclusive guide on the changes (Kurt Lewin, 2020). The below picture is just a general idea to conceptualize the model.
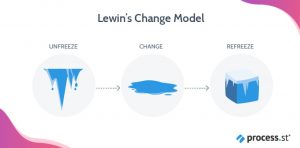
Fig 1: Unfreeze – Change – Refreeze (Kurt Lewin, 2020).
- Unfreeze – This is the first stage where thoughts are put forward as to why the change is necessary by stating the failures in current ideologies which is becoming a burden for the company (Kurt Lewin, 2020). The first part is always the hardest as a new daily operations procedure must be followed and the equilibrium is lost (Kurt Lewin, 2020). This is when the core of the organization must be scrutinized which creates a crisis that can be controlled (Kurt Lewin, 2020). This drives the motivation for change and the motivation for the change must drive for the changes to occur (Kurt Lewin, 2020).
- Change – Change does not happen overnight and it takes a while for the employees to get accustomed to it as well (Kurt Lewin, 2020). The change would have brought in a sense of ambiguity and to resolve this ambiguity, people must believe in actions leading them to a new path (Kurt Lewin, 2020). It is to be noted that it takes different timings for people to get used to it (Kurt Lewin, 2020). Time and communication are vital for the changes to happen successfully (Kurt Lewin, 2020).
- Refreeze – When the changes are taking place and people are becoming used to the new normal then it would be time to refreeze (Kurt Lewin, 2020). This stage needs to help people to institutionalize to obtain stability in the organization (Kurt Lewin, 2020). With stability, employees feel assertive and relaxed while working with the new ways (Kurt Lewin, 2020).
Here is the video on Lewin’s change management model:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uhrbO7lrHro&t=3s
John Kotter’s change management model: Kotter’s model has 8 steps as follows:
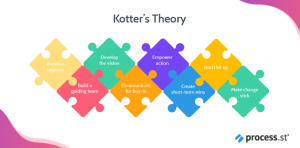
- Create urgency – Initial motivation is required to create urgency and this can be done by exhibiting poor sales statistics or bad financial conditions (John Kotter, 2020). Have an open discussion with the on-going changes and if many people get involved into it. It will feed upon itself (John Kotter, 2020).
- Form a powerful coalition – Identify key stakeholders and leaders and put forth the ideas and the changes with supporting research which will make things different and better (John Kotter, 2020). It is crucial to pull the influential people in the organization and work together (John Kotter, 2020).
- Create a vision for change – A clear vision that is change centric is an absolute necessary (John Kotter, 2020). Then a strategy is required to bring the vision into action with the help of coalition team (John Kotter, 2020).
- Communicate with vision – Communication must be powerful and frequent (John Kotter, 2020). It’s important to be open, honest and address people’s concerns (John Kotter, 2020).
- Remove obstacles – If there are any processes or people in the way for the change management they need to be removed or replaced in order to execute change management (John Kotter, 2020). By doing this, people feel empowered. It is also vital to keep a check on barriers during the execution (John Kotter, 2020).
- Create short term wins – During early change process, give the company the taste of victory by rewarding the people who met the targets (John Kotter, 2020). Create short term targets and long term goals and put in efforts to meet them (John Kotter, 2020). By consecutive success stories motivation among employees can be observed (John Kotter, 2020).
- Build on change – Keep building on the long term goals and don’t let quick wins make you stop (John Kotter, 2020). Set goals and learn about kaizen, a continuous improvement idea (John Kotter, 2020).
- Anchor the changes in corporate culture – Continuous efforts must be put to observe the changes in all parts of the organization (John Kotter, 2020). Talk about the success stories and progress in the organization (John Kotter, 2020). Key members must be given public recognition and keep everyone accountable (John Kotter, 2020). While hiring or training staff, new ideas must be included (John Kotter, 2020).
Here is the video on Kotter’s change management model:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xNILBjjVttA&t=140s
ADKAR Change Management Model:
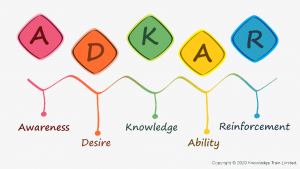
Awareness: Announce the change to employees before it was implemented and explain the reason for the change to the employees. Provide an opportunity to employees to ask questions and give suggestions. (Lucid, 2019)
Desire: Analyze employees’ reaction to the change. Some of them don’t fully support the change so the management need to make understand the employees that how the change benefits them. (Lucid, 2019)
Knowledge: The next step of ADKAR model is to provide training to their employees. The more knowledge and training give more employees understand the change and see the benefits of making the change. (Lucid, 2019)
Ability: Company needs to schedule practice runs before the change is fully implemented. Monitor performances and constructive feedback to set goals and metrics. (Lucid, 2019)
Reinforcement: Monitor the change for some time to ensure that new change fulfills the desired outcome. Use positive feedbacks to encourage employees to keep following the new change. (Lucid, 2019)
ADKAR change management video link:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oMiI59NMO2Q
Benefits of Change Management:
Benefits of change management by Prosci is divided into 5 perspectives and we look on them one by one:
- Three people-side ROI factors – Benefit perspective 1
The three people-side ROI factors are added to business case which is used to highlight the importance of change management. It focuses on:
- Clearly define the individual changes required by the project during the beginning phase (Prosci, n.d.).
- Use change management tool for delivering results in concrete terms for business (Prosci, n.d.).
- In terms of people side of change, elevate the discussion and document assumptions early in the process (Prosci, n.d.).
- Cost avoidance – Benefit perspective 2
If changes are poorly managed significant losses happen to the company. The costs happen at project and organizational levels.
- Costs to the organization if change is poorly managed:
- Productivity plunges [deep and sustained] (Prosci, n.d.).
- Impact on customers (Prosci, n.d.).
- Impact on suppliers (Prosci, n.d.).
- Loss of valued employees (Prosci, n.d.).
- Morale declines (Prosci, n.d.).
- Decline in quality of work (Prosci, n.d.).
- Resistance to change (Prosci, n.d.).
- History of failed change (Prosci, n.d.).
- Stress, confusion and fatigue (Prosci, n.d.).
- Change saturation (Prosci, n.d.).
- Costs to the project if change is poorly managed:
- Project delays (Prosci, n.d.).
- Missed milestones (Prosci, n.d.).
- Project put on hold (Prosci, n.d.).
- Resources not made available to project team (Prosci, n.d.).
- Budget overruns (Prosci, n.d.).
- Obstacles appear unexpectedly (Prosci, n.d.).
- Rework required on project design (Prosci, n.d.).
- Project fails to deliver on objectives (Prosci, n.d.).
- Project is fully abandoned (Prosci, n.d.).
- Loss of work by project team (Prosci, n.d.).
- Costs if the change is not implemented:
- Expenses not reduced (Prosci, n.d.).
- Efficiencies not gained (Prosci, n.d.).
- Revenue not increased (Prosci, n.d.).
- Market share not gained (Prosci, n.d.).
- Waste not eliminated (Prosci, n.d.).
- Regulations not met resulting in fines and penalties. (Prosci, n.d.).
- Risk mitigation – Benefit perspective 3
The potential risks about the project or change must be highlighted and a structured format must be followed to avoid it. [Specifically people side risks] (Prosci, n.d.). Usually, the financial and technological factors are considered (Prosci, n.d.).
- Benefits realization insurance – Benefit perspective 4
Most of the strategic changes in the organization depends on how people do their jobs (Prosci, n.d.). Always look at how the objective is dependent on people doing their jobs in a different manner (Prosci, n.d.). Implementing a structured change format is like taking out an insurance for the project (Prosci, n.d.).
- Probability of meeting objectives – Benefit perspective 5
The more effective the change management is, the more the objectives are met (Prosci, n.d.). Working with thousands of change management professions across the globe, the graph below exhibits that projects with exceptional change management are six times more likely to meet objectives than their counterparts (Prosci, n.d.).
Also, the organization loses the investment made in the project when the project does not deliver results.
Shown below is the correlation of change management effectiveness with meeting objectives.
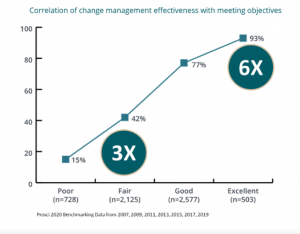
Fig 2: Correlation of change management effectiveness with meeting objectives (Prosci, n.d.).
When is Change Management Required & What are Its Impacts?
The organizational change management is required whenever an enterprise is undertaking an even which will have an impact on the firm’s daily operations (Perkins, Bart, 2018). When a change management occurs it would impact the three scenarios states below:
- The work content of individual jobs: Many jobs require monotonous work to be done and employees become accustomed to it (Perkins, Bart, 2018). For instance, the accounting department will have a set of daily, weekly, monthly and yearly tasks and even a small change in schedule will have an impact on its daily operations (Perkins, Bart, 2018).
- The roles of individual employees: Many people will be excellent technically like programmers or security specialists but when it they are put to test in positions apart from their comfort zone, they might struggle (Perkins, Bart, 2018). This is when few employees can question the management about their credibility (Perkins, Bart, 2018).
- The organization itself: People working in executive positions will know when the changes will happen and would have gotten a head start (Perkins, Bart, 2018). Basically, they would be ready for the change but on the other hand, people working as employees will get to know only when it is executed within the organization and they will not have the turnaround time to get adapted to the changes as they would be less prepared (Perkins, Bart, 2018).
Role of HR in Change Management
A Role of Watchdog: HR department plays an important role in thinking organizational design to bring change and facilitate the implementation of these new processes. This implies that HR department has crucial monitoring role. During these phases of change, HR department ensures that the company’s cultural integrity and processes are coherent and harmonious.
Taking Time to Communicate: As HR gain in expertise and business intelligence, it is important for them to share their strategic vision with finance and marketing as well as other departments of the organization. HR’s central function in the management of people and talent means they can easily influence change adoption through strategic HR policies in the fields of remuneration, succession and hiring.
Establishing a Change Agenda: HR should recommend and define specific milestones to be reached by both the organisation and its employees through time. Business transformation takes time. If rushed, could inevitably end up in a costly failure. So, taking it step by step HR department will ensure that employees understand fully to these changes.
Training Managers: It is important to train managers to become good change agents. This should be done before business transformation happens, but so that they understand the pros and cons of the change they are contributing to their effort. HR department should provide them with a meaning and purpose to engage in the business transformation. Also, actively listening to the managers is essential to accompany them through the different challenges they face.
Proposing Adapted Solutions: Depending on whether change is required to adapt in a highly competitive market or due to a phase of growth, HR should propose adequate solutions to each situation.
Important Website and Video Links
- Change Management (Prosci.com): https://www.prosci.com/resources/articles/what-is-change-management
- Change Management Processes (SHRM): https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/managingorganizationalchange.aspx
- Change Management (YouTube): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=__IlYNMdV9E
- Organizational Change Management (YouTube): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ir_7a3fgpFQ
- How to Lead Change Management (YouTube): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PQ0doKfhecQ
Key Takeaways
- You will be be able to explain what is change management and how it can be implemented in organizations.
- Illustrate the 4 principles of change management
- Get an understanding of three models of change management which are Lewin’s, Kotter’s and ADKAR.
- Explain the benefits of change management.
- Demonstrate when the change is necessary in the organization and what would be its impacts.
- Explain role of HR in change management
- Some helpful website and video links
REFERENCES:
- Gerbec, M. (2017). Change management. Safety change management – A new method for integrated management of organizational and technical changes, 225-234. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2016.07.006
- John Kotter. (2020). John Kotter’s 8 Step Change Model. Retrieved from https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_82.htm.
- Kurt Lewin. (2020). Kurt Lewin’s Change Management Model. Retrieved from https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_94.htm.
- MindTools. (2020). What is Change Management. Retrieved from https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_87.htm.
- Perkins, Bart. (2018, 04 12). What is Change management? A guide to Organizational Transformation.
- Prosci. (n.d.). Cost-Benefit Analysis of Change Management. Retrieved from https://www.prosci.com/resources/articles/cost-benefit-analysis-change-management.
- Lucid. (2019, October 11). Using the ADKAR Model for Change Management. Using the ADKAR Model for Change Management | Lucidchart Blog. https://www.lucidchart.com/blog/using-the-adkar-model-for-change-management
- Perrin, O. (2017, January 14). The Role of HR in Managing Change in the Workplace. Employee Connect HRIS. https://www.employeeconnect.com/blog/hr-role-change-management/
