10 Future Simple, Future Continuous, and Future Perfect
Past, present and future
Annapurna Madhuri
Introduction:
Any action or an event that will have occured or been completed at some point in future, telling us that the events will already have happened before another completed action or at a certain time in future, is expressed in the future perfect tense.
Here we have to understand the two aspects
- The action contains a sense of completion.
- Indicates the time of completion of action in future. The action will be completed in the future?
The future perfect tense form of a verb has two parts:
- The future tense form of ‘to be’ – known as helping verb or auxillary verb – will/shall
- Past participle form of the main verb.
The structure of the sentence:
Affirmative sentences:-
Subject + helping verb + main verb + specific time
Example 1: Sneha will have finished her work by tomorrow morning.
Subject+ will have + main verb (in past participle form) + completion of another action
Example 2: Anu will have published ten papers by the time she finishes her Ph.D.
Interrogative sentences:-
Helping verb + subject + main verb in the past participle form + specific time in future
Example 1: Will Sneha have finished her work by tomorrow morning?
Will + subject + have + past participle form of main verb + another action in future
Example 2: Will Anu have published ten papers by the time she finishes her Ph.D.?
Negative sentences:-
Subject + helping verb + NOT – main verb in past participle form + specific time of completion
Example 1: Sneha will not have finished her work by tomorrow morning.
Subject + will NOT have + participle form of main verb + another event in further future.
Example 2: Anu will NOT have published ten papers by the time she finishes her Ph.D.
Learning Objectives
At the end of this chapter, all learners will be able to
- Use auxiliary (helping) verbs with the past participle form of the base verb.
- Distinguish between usage of simple future and future perfect forms of verbs.
- Use verbs in future perfect tense in affirmative, interrogative and negative sentences.
Quick Read
Read the paragraph below:
Ms. Anu is a teacher. In April 2020, she will have completed 22 years working as a teacher. She teaches Economics for the higher secondary students. She is also a guidance counsellor. By the time she reaches school, students are already waiting for her. She will have spoken to most of them before she takes her regular classes. Ms. Anu will have handled most of her counselling sessions for the day by lunch time.
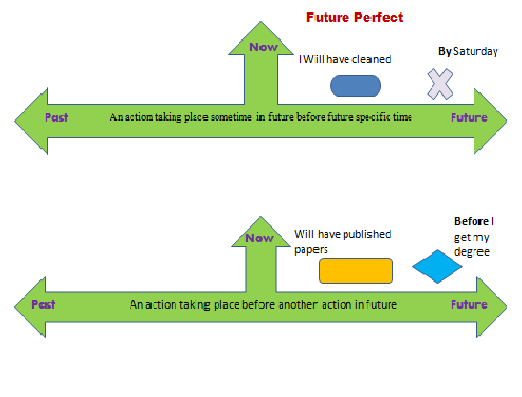
Future perfect tense is used when we have to talk about actions indicating a sense of completion at a certain time in future. These actions take place
- before another action in future.
- before a specific time in future.
Note: Future perfect is always used with past participle of a verb indicating a sense of completion of the task on looking back at the activity from some point further in future.
Past participle forms – Please refer to the list.
Exercise:
Focus:
Summing up:
Future perfect tense is used to express
Signal Words:
Complete the sentences in the future tense, taking hint from the signal words.
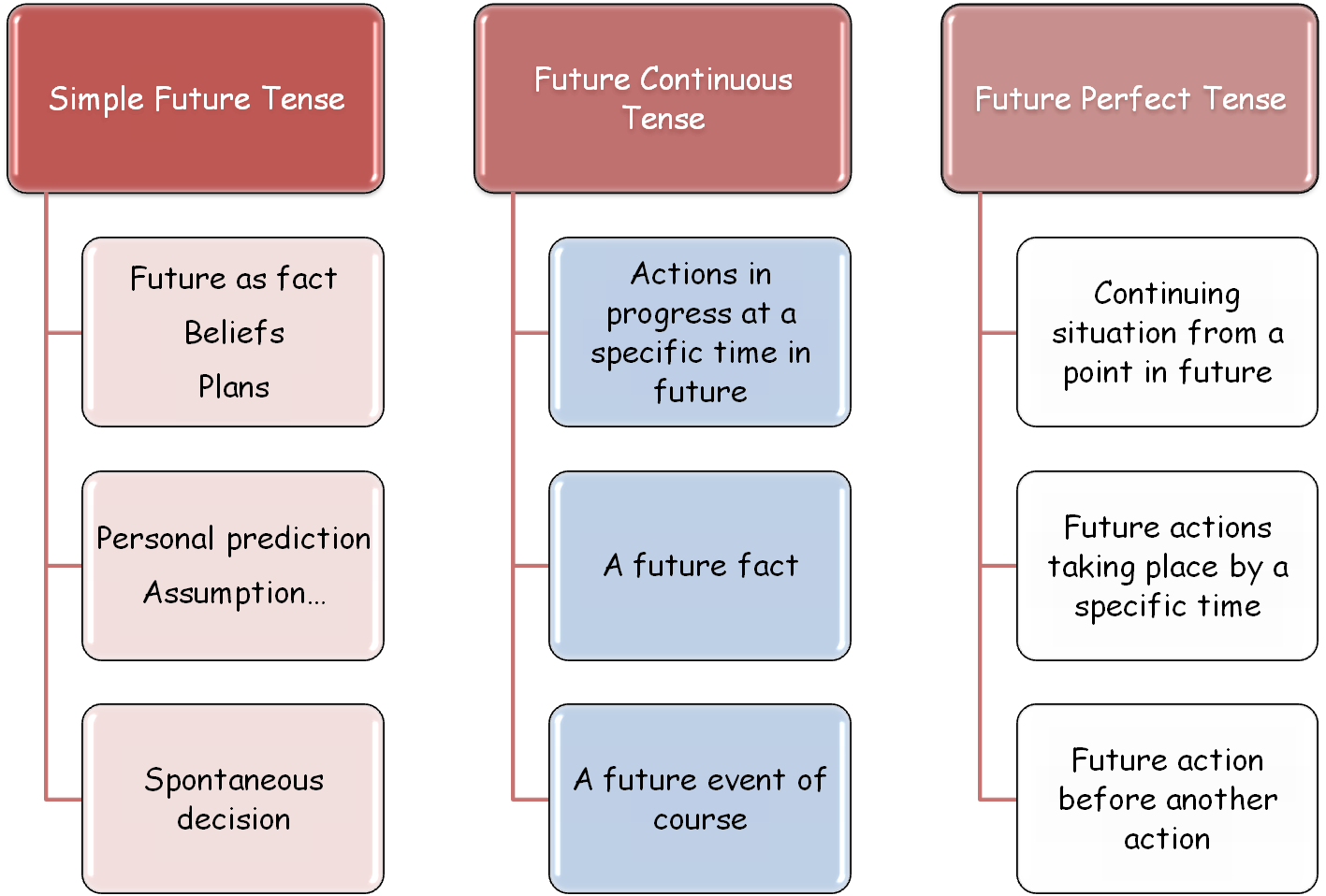
Simple future, future continuous, future perfect: Differences
Interrogative and Negative sentences in present perfect tense
Exercise: Change to interrogative sentences
Exercises: Change to negative sentences
Additional Self Check Exercises:
- Choose the correct form of the verb
- Identify tenses used in the following sentences –