Appendix: The Marketing Plan
Appendix 1.1 The Marketing Plan
Learning Objectives
- Role of marketing plans in organizations.
Much as firms must set their customers’ expectations, marketing managers must set their organization’s marketing expectations. Marketing plans help them do that. A well-designed marketing plan should communicate realistic expectations to a firm’s CEO and other stakeholders. Another function of the marketing plan is to communicate to everyone in the organization who has what marketing-related responsibilities and how they should execute those responsibilities (Maddox, 2007).[1]
Katie Scallan-Sarantakes develops and executes marketing plans for the Gulf States region of Toyota. Her path to this position is not unusual. Listen as she describes what she did to prepare herself for a position running a regional marketing office of a major global automaker.
Who, within an organization, is responsible for creating its marketing plans? From our discussion above, you might think the responsibility lies with the organization’s chief marketing officer (CMO). The reality is that a team of marketing specialists is likely to be involved. Sometimes multiple teams are involved. Many companies create marketing plans at the divisional level. For example, Rockwell International has so many different business areas that each does its own strategic planning. The division responsible for military avionics, for instance, creates its own marketing plans and strategies separately from the division that serves the telecommunications industry. Each division has its own CMO.

Some of the team members specialize in certain areas. For example, the copier company Xerox has a team that specializes in competitive analysis. The team includes an engineer who can take competitors’ products apart to see how they were manufactured as well as a systems analyst who tests them for their performance. Also on the team is a marketing analyst who examines the competition’s financial and marketing performance.
Some marketing-analyst positions are entry-level positions. You might be able to land one of these jobs straight out of college. Other positions are more senior and require experience, usually in sales or another area of marketing. Marketing analysts, who are constantly updating marketing information, are likely to be permanent members of the CMO’s staff.
In some consumer-goods companies with many brands (such as P&G and SC Johnson), product—or brand—managers serve on their firm’s marketing planning teams on an as-needed basis. These individuals are not permanent members of the team but participate only to the extent that their brands are involved. Many other members of the firm will also participate on marketing planning teams as needed. For example, a marketing researcher is likely to be part of such a team when it needs data for the planning process.
Key Takeaways
The CMO of a business unit is likely to be responsible for the creation of its marketing plan. However, the CMO is generally assisted by marketing professionals and other staff members, who often work on marketing planning teams as needed. Marketing analysts, however, are permanent members of the CMO’s staff.
Find a summary of the marketing planning roles in the below hotspot image:
Review and Reflect
- Who is involved in the creation of a marketing plan?
- In addition to marketing analysts, what other members of an organization help create marketing plans?
Media Attributions
- MAPS Air Museum © 5chw4r7z is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
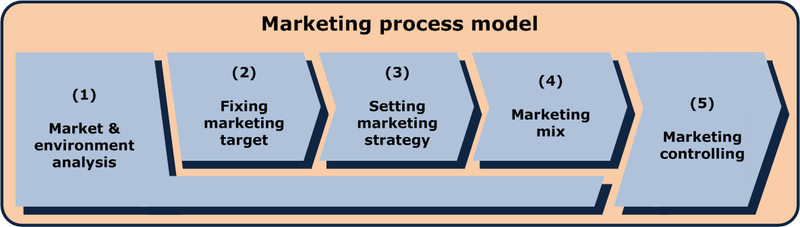
- Marketing process model © Grochim is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
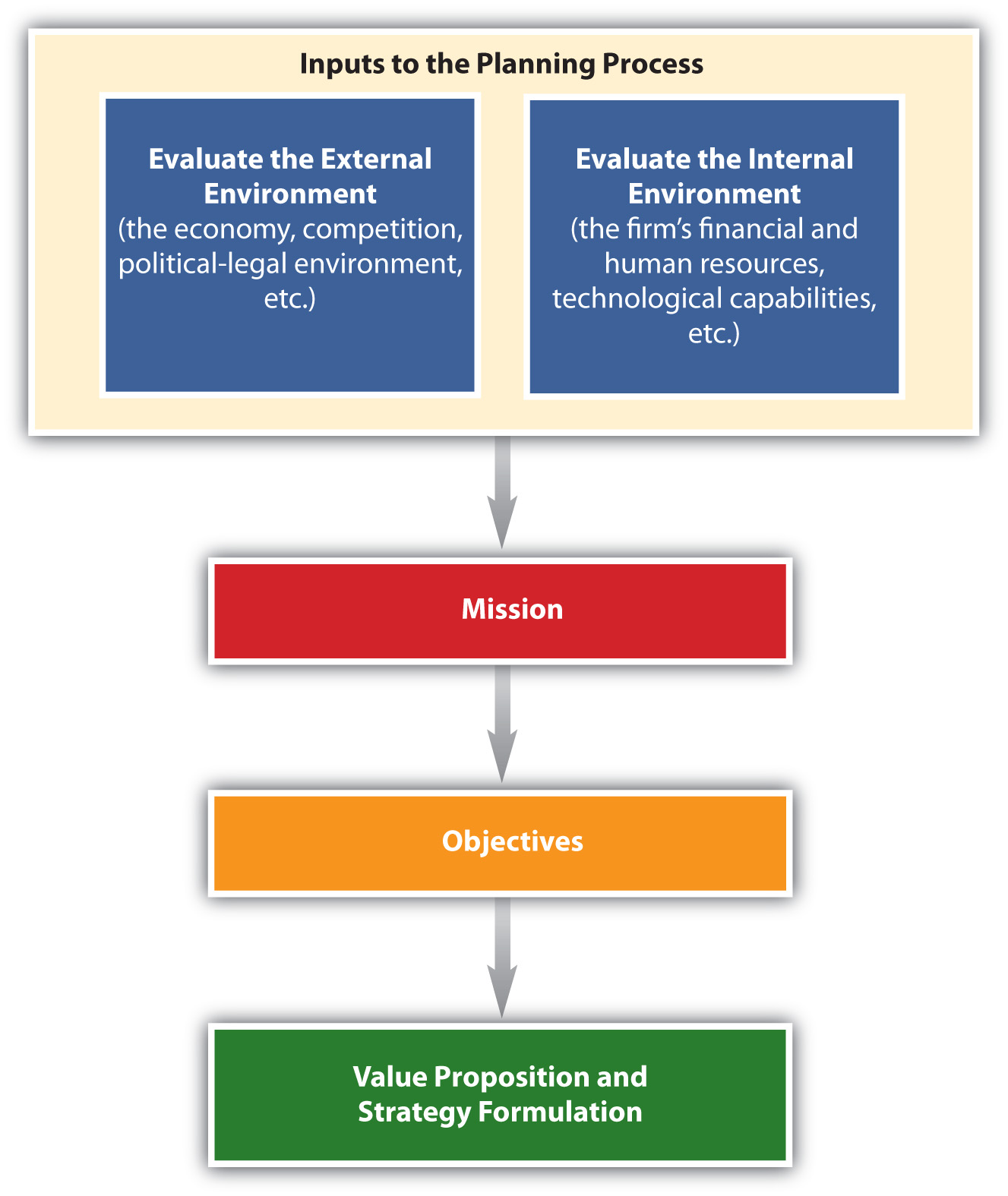
- Steps in Creating a Marketing Plan © Unknown is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
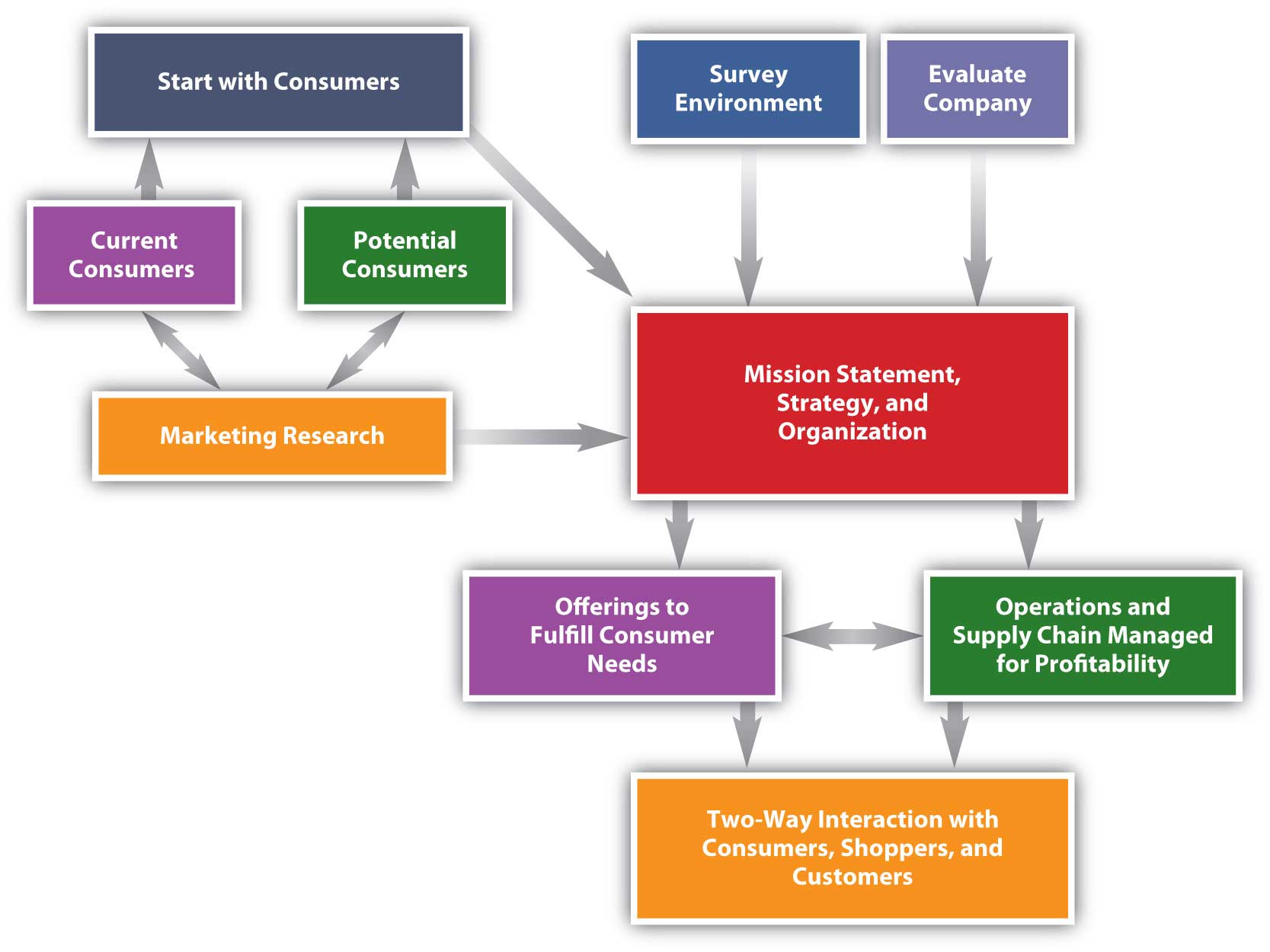
- Marketing Planning Graphic © Lumen Learning is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
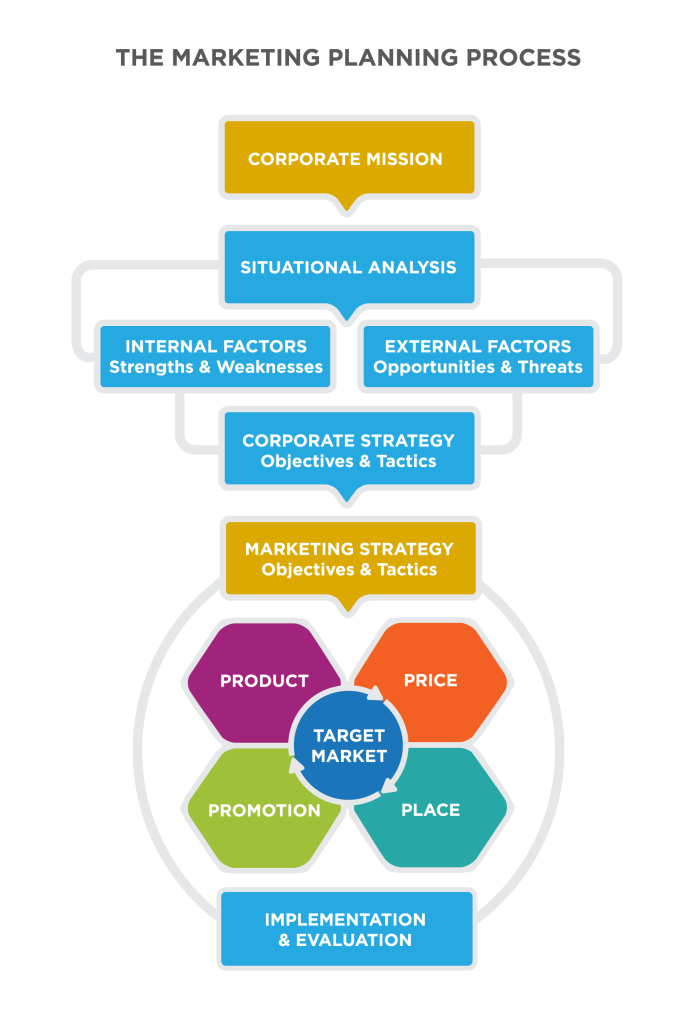
- The Strategic Planning Process © Anonymous is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- Maddox, K. (2007, December 10). Bottom-line pressure forcing CMO turnover. B2B, 92(17), 3–4. ↵
a strategic plan at the functional level that provides a firm’s marketing group with direction

