Chapter 7: Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives
7.2 Preparation of Carboxylic Acid
The methods to prepare carboxylic acids can be generally divided into three categories: oxidation reaction, Grignard reaction and hydrolysis of nitrile.
7.2.1 Preparation of Carboxylic Acid by Oxidation
Since the carboxyl group COOH is in the high oxidation state, it can be prepared by oxidation of other functional groups in the lower oxidation states, for example, alkene, alcohol, and aldehyde (refer to section 10.7 in Book I, for oxidation states of organic compounds). We have learned all these oxidation reactions in earlier sections, summaries are provided here.
Oxidation of Alkenes (refer to section 10.7 in Book I)
The oxidative cleavage of C=C double bond with potassium permanganate, KMnO4, under hot basic conditions, could produce the (salt of) carboxylic acid if the structure of the alkenes is appropriate.
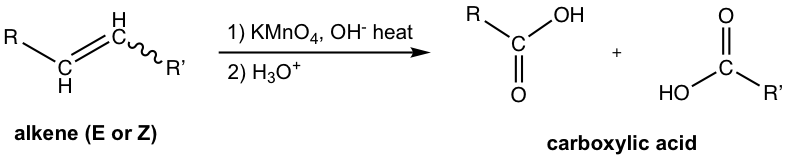
For symmetric alkenes (R and R’ are the same), only one carboxylic acid is generated as a product and this method can be applied effectively for preparation.
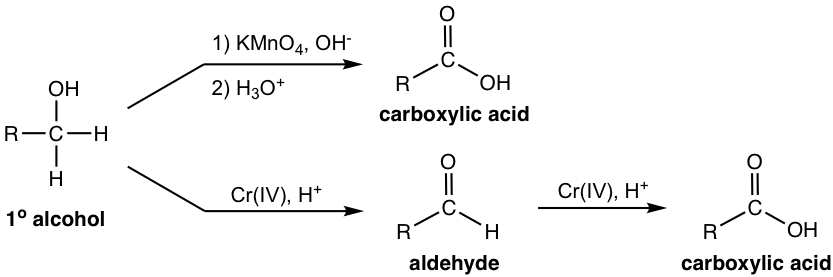
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols and Aldehydes (refer to section 1.2.5)
When primary alcohols are oxidized by potassium permanganate KMnO4 in basic condition, (salt of) carboxylic acid is produced. Under the acidic condition with Cr (VI) reagents (CrO3, or H2CrO4), primary alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes first, then to carboxylic acids as final products.
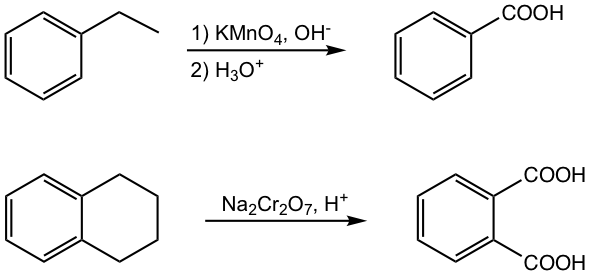
Oxidation of alkylbenzenes (refer to section 5.3.2)
The alkyl group (the group must have the hydrogen in the benzylic position) attached to a benzene ring is oxidized to carboxylic acid by potassium permanganate KMnO4 in basic condition, or sodium dichromate Na2Cr2O7 in acidic solutions.
7.2.2 Preparation of Carboxylic Acid by Grignard Reaction with CO2 (refer to section 1.5.4)
The reaction between Grignard reagent and carbon dioxide (CO2), followed by acidic work-up, produces carboxylic acid. Since Grignard reagents are compatible with a variety of groups, this method can be used to synthesize carboxylic acid with a variety of different structures.
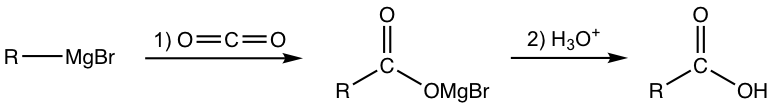
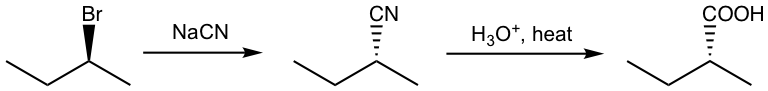
7.2.3 Preparation of Carboxylic Acid by Hydrolysis of Nitrile
As mentioned nitriles are considered carboxylic acid derivatives because they can be converted to carboxylic acid by hydrolysis. Nitriles can be prepared by either the SN2 reaction of halides with sodium cyanide, or the addition of aldehyde with sodium cyanide followed by protonation.
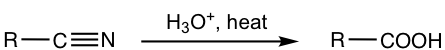
A specific example is given here: