3 Describe the differences between a regressive and progressive tax. Provide some examples of each in Canada.
Cynara Almendarez
Regressive taxes are applied uniformly, and they do not change based on an individual’s level of income. A regressive tax system affects low-income taxpayers more than high-income taxpayers because it takes a higher percentage of their earnings.
A great example of a regressive tax is the 5% Goods and Services Tax (GST). For example, say a doctor earns $175,000 annually and a retail worker earns $30,000 annually. They both purchase a laptop for $1,000, and are charged $50 GST ($1,000 X 5%). Although the $50 GST amount is the same for both the doctor and the retail worker it is a higher percentage of the retail workers overall income. This is known as a regressive tax because it has a larger percentage impact on lower income individuals.
![The GST for the retail worker's income is calculated as [($50/$30,000) x 100]](https://kpu.pressbooks.pub/app/uploads/sites/162/2019/04/2019-03-14-7-1-300x135.png)
![The GST for the doctor's income is calculated as [($50/$175,000) x 100]](https://kpu.pressbooks.pub/app/uploads/sites/162/2021/01/2019-03-14-7-300x143.png)
Progressive taxes are the opposite of regressive taxes. Progressive taxes increase based on your taxable income. Canada has a progressive income tax system; therefore, high-income taxpayers pay a progressively higher percentage of tax than low-income taxpayers.Using our previous example, because of the doctor’s higher annual income, the doctor will have to pay more taxes than the retail worker based on Canada’s federal tax rates of 2018.
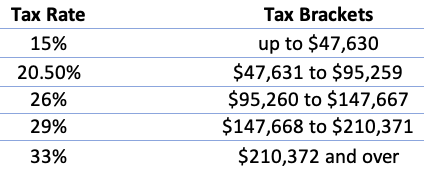
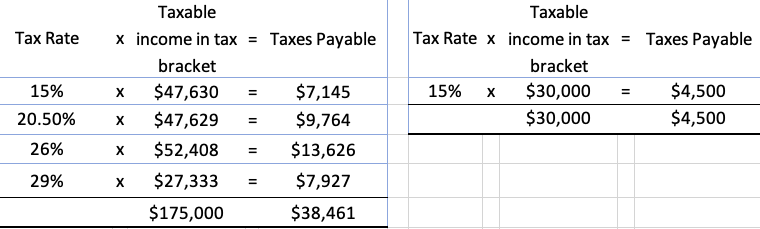
The doctor will have to pay $38,461 in taxes (an average tax rate of 21.98%) while the retail worker will only have to pay $4,500 of taxes (an average tax rate of 15%). Progressive taxes get progressively higher as your taxable income increases.
Doctor Teacher
Interactive Content (Author: Cynara Almendarez, January 2019).
Interactive Content (Author: Joyce Hards, April 2019)
References and Resources:
- Article – “Canadian Income Tax Rates for Individuals – Current and Previous Years” (Author: Government of Canada)
- Competency map: 6.1.1
January 2019
Media not mentioned below is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA(Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) and owned by the author of the text.

