14 Plant Morphology – Leaves
Learning Objectives
- Describe the morphological characteristics of plant leaves.
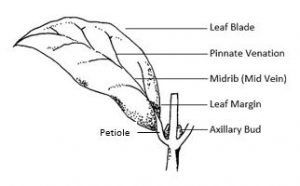
Leaves are specialized structures for photosynthesis that provide plants with energy. Leaves arise at nodes just below an axillary bud on woody stems and are usually petiolate, that is composed of a blade and stalk-like petiole. Petioles may have stipules, two small leaf-like flaps that are attached at the base. In some cases, stipules on leaves and stems may become modified into spines, thorns, or prickles. Some leaves are sessile, that is, they lack petioles and have blades directly attached to the stem. When a bud is located in the axil of a single leaf and the stem, as shown in Figure 14.1 the leaf is classified as simple.
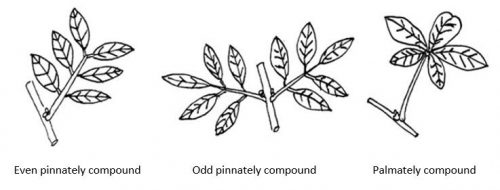
However, when a bud is located in the axil of a structure with more than one leaf (leaflet) on attached to the axis (rachis), the leaf is classified as compound. As shown in Figure 14.2, even or odd numbers of leaflets may be pinnately compound that is, arranged along a central axis (feather-like), or palmately compound from one point on the tip of the petiole, (like fingers on an out-stretched hand). Compound leaves may undergo double (bipinnate) or triple (tripinnate) compounding into finer segments or leaflets.
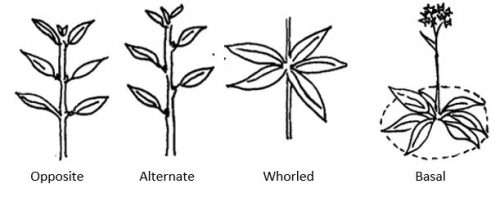
Phyllotaxy, the arrangement of a leaf or bud in relation to another leaf or bud along a plant stem is a useful basis for classifying plants. Figure 14.3 illustrates common leaf arrangements where leaves and buds on a stem are opposite (directly across from each other on the stem), alternate (spaced alternately along the stem axis), whorled (three or more leaves and buds are positioned at a node), or basal (emerging from the base). Leaf arrangement may also be described as spiral, clustered, decussate (alternating pairs at right angles), and imbricate (overlapping scales).
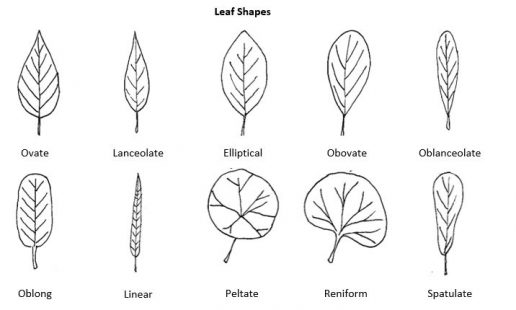
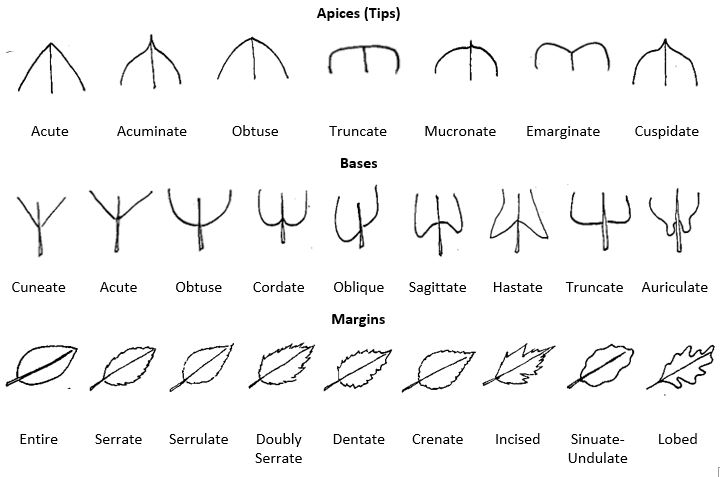
Leaf venation refers to the patterns of veins within the leaf blade. In eudicot plants, leaf venation is typically either pinnate or palmate and may have multiple branching that gives an overall netted appearance. In contrast, monocots will have parallel leaf venation. Additional morphological features for description include leaf shape, tip and base features, and margins (edges). Leaf surface characteristics vary and some may be smooth (glabrous) or with hairs (hirsute or pubescent), wrinkles (rugose), pustules (verrucose) or other interruptions of the surface. Additional leaf surface terms are defined at this link to Leaf [New Tab][1].
Figure 14.4 and Figure 14.5 illustrate components of a leaf morphology chart commonly used for plant identification. More detailed information about the external characteristics of leaves is available at this link to Leaf Morphology [New Tab][2].