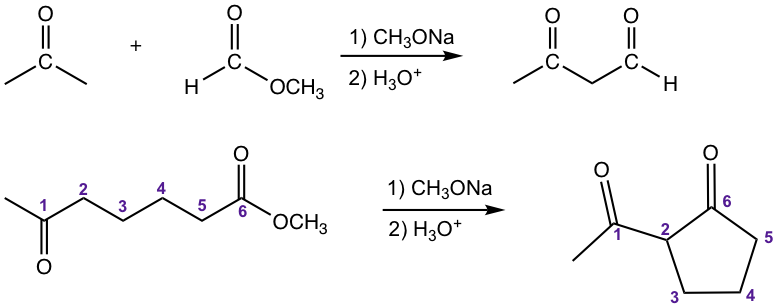Chapter 8: The Claisen Condensation and Applications in Synthesis
8.2 Other types of Claisen Condensation
8.2.1 Intramolecular Claisen Condensation: the Dieckmann Condensation
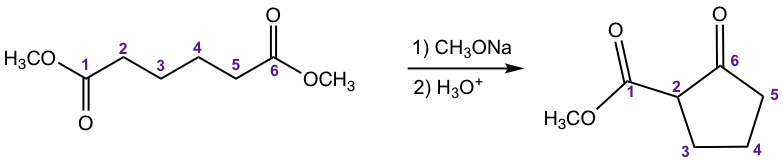
For a molecule that contains two ester groups, an intramolecular version of the Claisen condensation could occur, which is called the Dieckmann Condensation. Dieckmann condensation is favorable when a 5- or 6-membered ring is formed. An example is given below.
8.2.2 Crossed Claisen Condensation
Crosse Claisen condensation is the reaction between two different molecules.
Crossed Claisen Condensation between two Different Esters
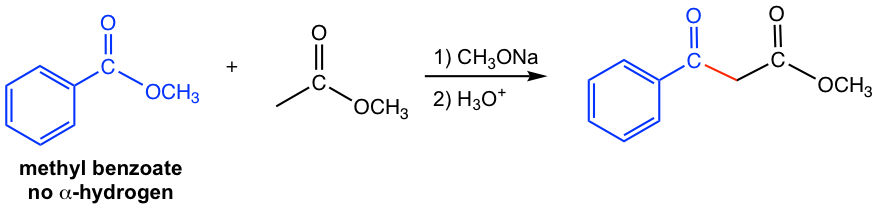
For the two esters, one ester has no α-hydrogen and the other ester has α-hydrogens. The ester with α-hydrogen becomes enolate in the presence of bases, and the enolate reacts with the carbonyl group in the other ester. As shown in the following example (Fig. 8.2b) that methyl benzoate is the ester has no α-hydrogen, it undergoes crossed Claisen condensation with the methyl acetate that has α-hydrogens.
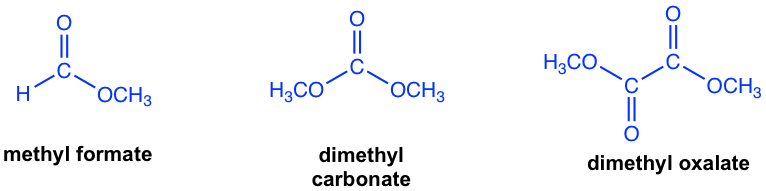
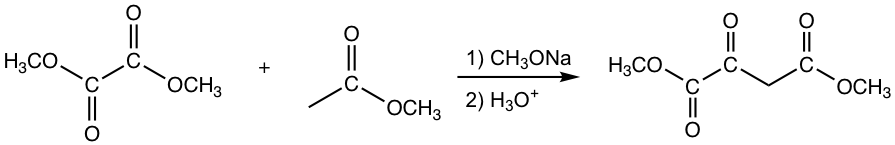
The other esters that have no α-hydrogen include formate, carbonate and oxalate, as the examples given in Fig. 8.2c.
Examples
Show the product of the following reactions.
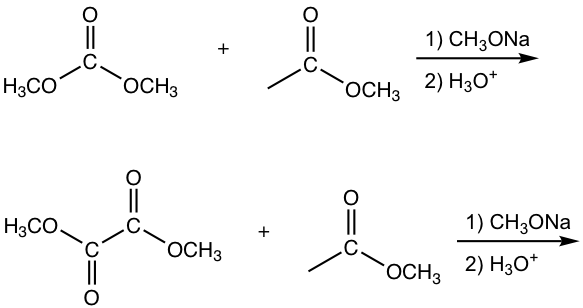
Answers:
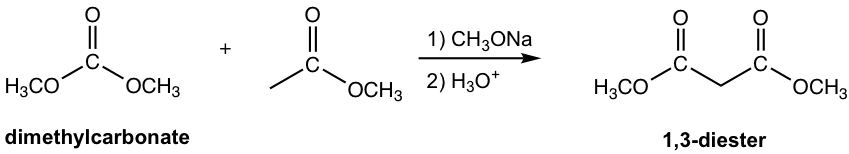
Note: 1,3-diester is formed for condensation with carbonate.
Crossed Claisen Condensation between Ester and Ketone
The other type of crossed Claisen condensation is between one ketone and one ester. The α-hydrogen of the ketone is more acidic than that in ester, therefore the ketone enolate is formed preferably and reacts with ester in acyl substitution. As shown in the following example 1,3-diketone is usually the product for such reaction.
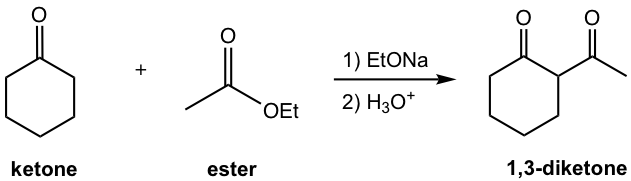
Examples
Show the product.
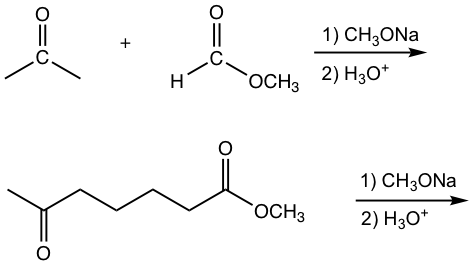
Answers: