Chapter 2: Aldehydes and Ketones
2.9 The Baeyer-Villiger Reaction
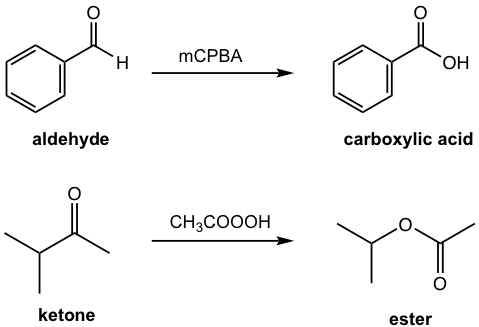
Baeyer-Villiger reaction is the oxidation of an aldehyde or ketone by applying peroxycarboxylic acid as the oxidizing agent. In the Baeyer-Villiger reaction, the aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid, and the ketone is oxidized to an ester. A couple of examples are given in Fig. 2.9a.
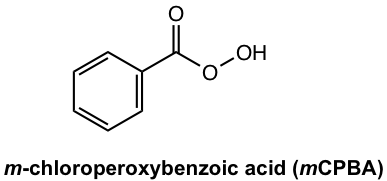
Peroxycarboxylic acid is a strong oxidizing agent, which has the peroxy group O-O. A common peracid used for the Baeyer-Villiger reaction is m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid, or mCPBA.
The mechanism for the Baeyer-Villiger reaction is shown in Fig. 2.9c.
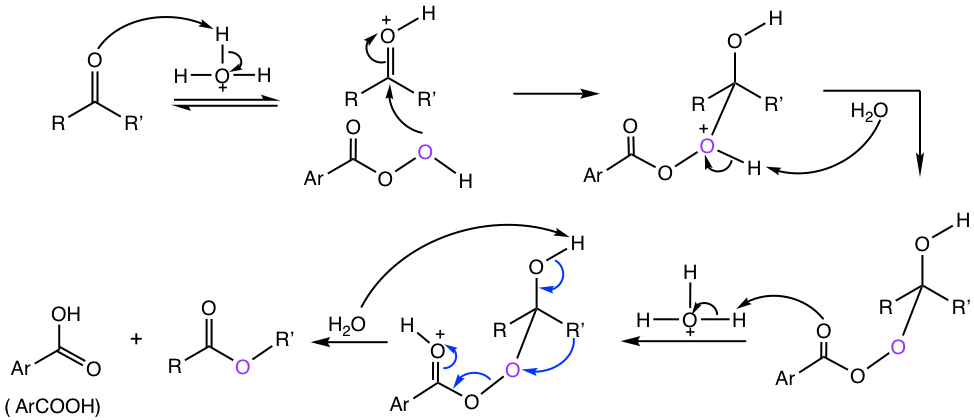
The group (R’ in the mechanism in Fig. 2.9c) migration is the key step in the mechanism. Different group has different tendencies for migration. It is shown from studies that the aptitude for migration is: H > Ar > 3° > 2° > 1° > methyl. For aldehyde, H migrates and results in carboxylic acid. For ketone, the migration group R’ will be the OR’ in the ester product.
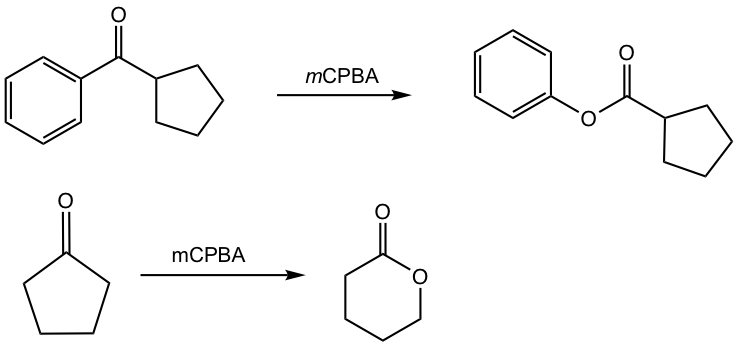
Examples
Show the product of the following reactions.
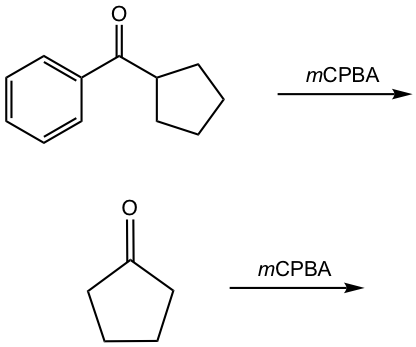
Answers: