Chapter 9: Carbohydrates
9.5 Degradation and Synthesis of Monosaccharides
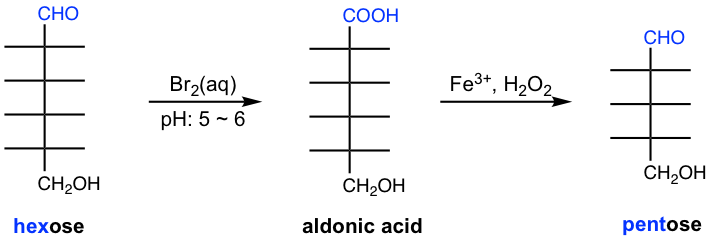
Ruff degradation is the method to shorten the chain of monosaccharides by one carbon atom. It is a process that involves two steps, in which aldose is oxidized by Br2(aq) to aldonic acid in the first step, and then oxidative decarboxylation occurs by H2O2 in the presence of Fe3+ to remove one carbon from the structure.
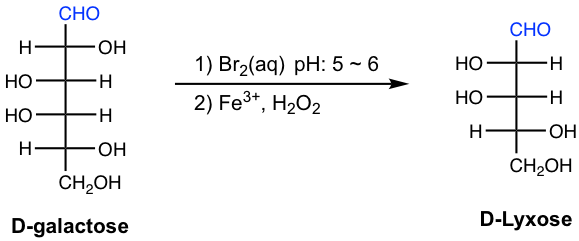
In the following example, D-galactose is degraded to D-lyxose by the Ruff procedure, and the configurations of all the other carbons remain the same.
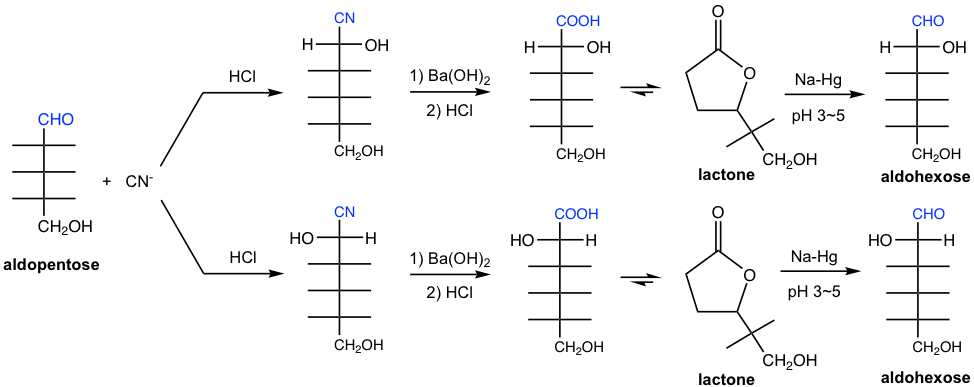
9.5.2 Kiliani-Fischer Synthesis
An aldose can be converted to epimeric aldonic acids having one additional carbon through the addition of HCN and subsequent hydrolysis of the cyanohydrins. The aldonic acids stay as lactones preferably, which is then reduced by Na-Hg at pH 3 ~ 5 to aldoses. This method for lengthening the carbon chain of an aldose is called the Kiliani-Fisher synthesis.