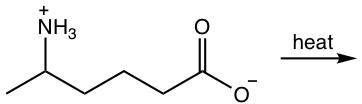
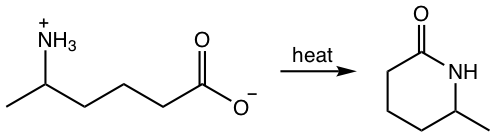
Chapter 7: Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives
7.6 Amides
Amide is the least reactive among the group of carboxylic acid derivatives. Being the least reactive one, amide can be prepared by starting from any of the other carboxylic acid derivatives, that is starting with acyl chloride, anhydride, acid, and ester.
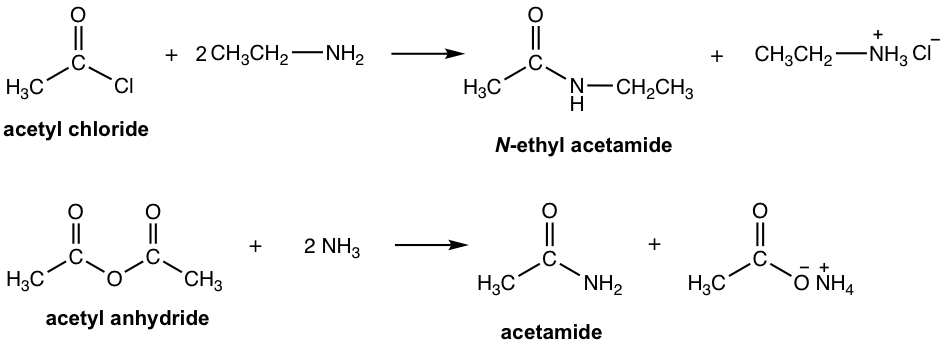
Starting from acyl chloride or anhydride, the reaction occurs readily with amines at room temperature to produce amide. The attention is that two equivalents of amines are required to neutralize the side acid product for both reactions (refer to the reaction summary in Fig 7.4b and Fig 7.4f). Two specific examples are given in Fig. 7.6a.
Starting from ester or carboxylic acid, heating is required to prepare amide because of the lower reactivity of these reactants. When acid reacts with amine, an acid-base reaction first occurs to produce the ammonium carboxylate salt, and the salt is converted to amide upon heating.
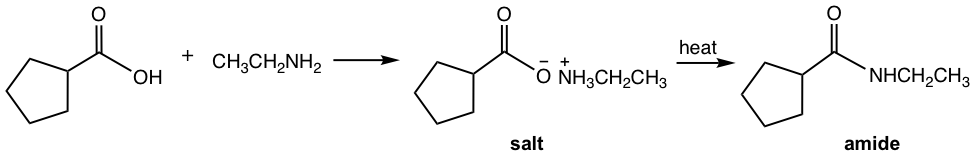
Examples