4. COURSE DESIGN & DELIVERY REVIEW
This section includes guidance to support the program review team to write chapter 4 of the self-study report. Refer to the Chapter 4 of the self-study guide (guide #4) and self-study report template as you review the following sections of this current guide (guide #2).
The program review team is also expected to incorporate results from external surveys (especially student and faculty surveys) as they write Chapter 4 of the self-study report. Please refer to Survey Development Guide (guide #3) as you review the following sections of this current guide (guide #2).
Refer to key principles discussed below to support the course design and delivery review portions of the program review process.
What is Constructive Alignment
Constructive Alignment (CA) hinges on the outcomes-based approach to course and lesson design. CA refers to the process of aligning Course Outcomes (CO) with Assessments (A) and Learning (L) activities designed to deliver a course or a lesson. Action verbs developed in Bloom’s Taxonomy are typically used to determine the complexity of the learning outcomes (lower order to high order skills) of a course/lesson. Assessment and learning activities should then be developed and aligned with the degree of complexity of the selected learning outcomes.
The diagram below will showcase the alignment between CO-A-L.
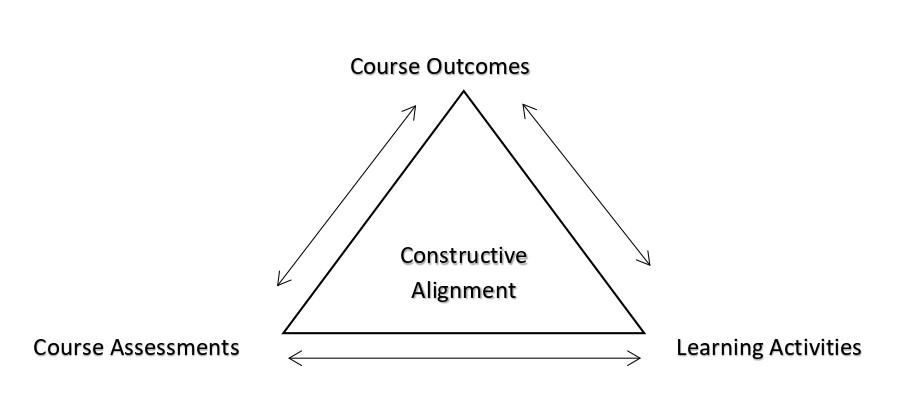
Here is a short video created by Gwenna Moss (Centre for Teaching and Learning at the University of Saskatchewan) that describes Constructive Alignment.
Example of Constructive Alignment
Here is an example (presented visually) that highlights the alignment between learning outcomes (based on action verbs related to Bloom’s Taxonomy complexity levels of thinking skills), assessment and learning activities.
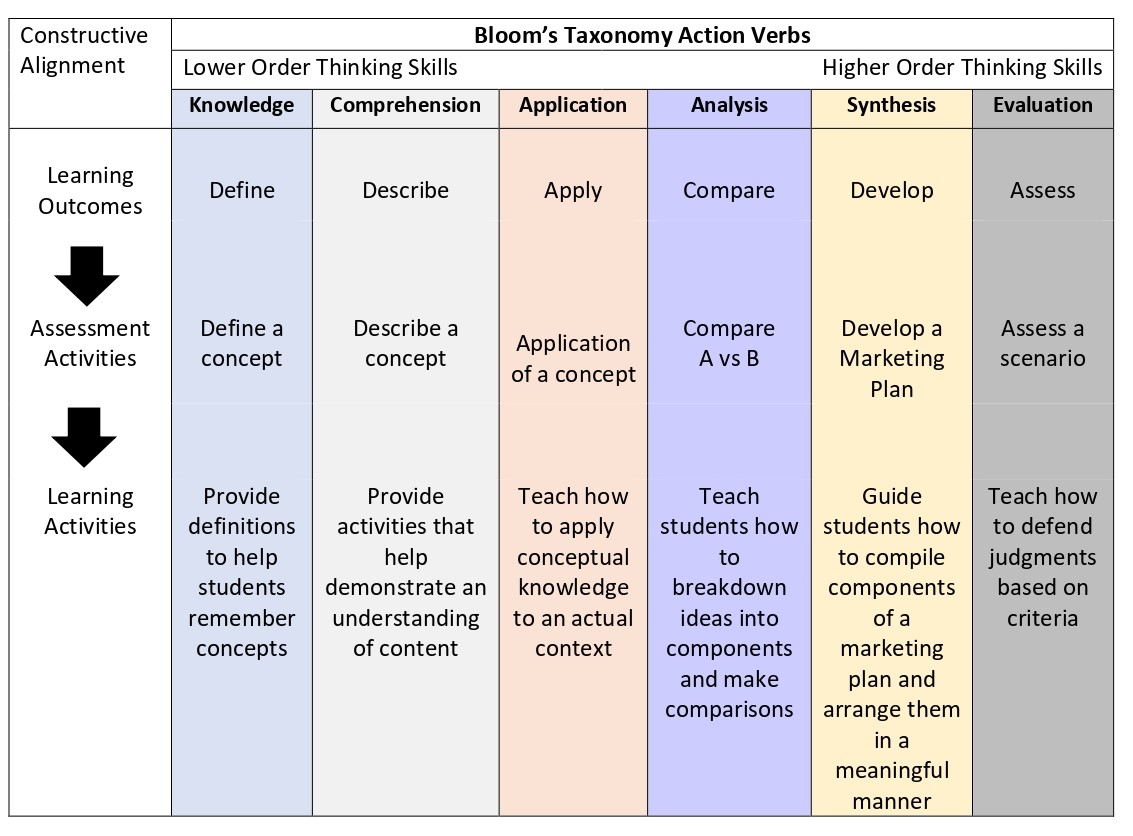
As you go through the above table from left to right, learning outcomes are arranged from lower order thinking skills (Knowledge, Comprehension) to higher order thinking skills (Synthesis & Evaluation). Notice the assessment & corresponding learning activities listed for each of the Bloom’s taxonomy thinking skill represents the level of complexity highlighted in that verb. For example, if the learning outcome is to get students to apply a given skill, then the assessment activity must refer to an application task. The associated learning activities should also be developed to assist students learn how to apply that concerned skill.
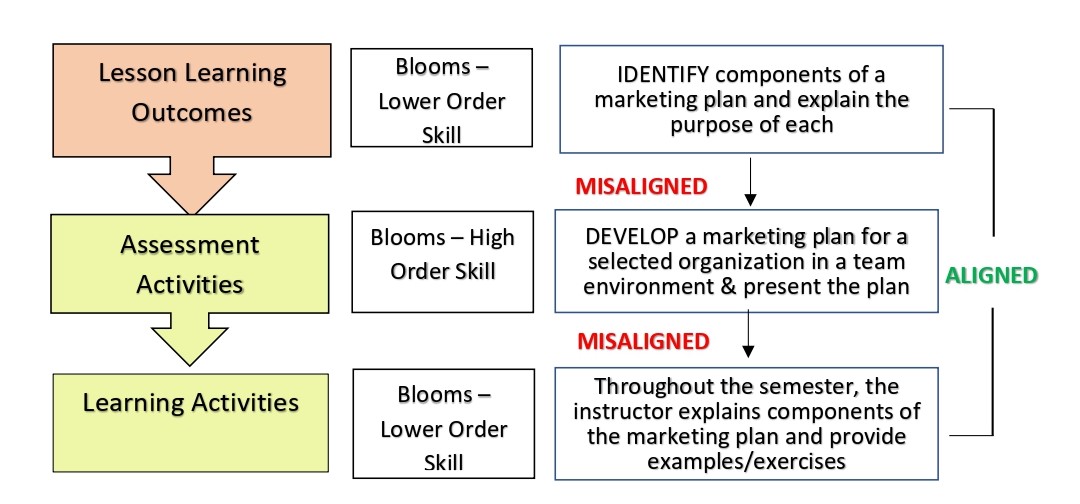
Example of Misalignment
See diagram below for an example of a misalignment.
The learning outcome calls for students to identify components of a marketing plan, which is the demonstration of a lower order thinking skill. As for the learning activity, the instructor is using a variety of examples/exercises explaining components of a marketing plan. The learning activities are constructively aligned with the learning outcome.
Notice the assessment calls students to develop a marketing plan which is the demonstration of a higher order thinking skill. Therefore, the assessment is not constructively aligned with the learning outcome nor the learning activities.
When designing a course, it is important to adhere to the principles of constructive alignment to make sure instructors deliver program and course outcomes to students in the form of well aligned lessons and assessments. Having reviewed this principle, the following sections will provide guidance to the program review team to assess the constructive alignment of courses developed in the program under review.
Constructive Alignment of Your Courses
To determine whether courses within a program meets quality standards, the program review team must assess whether course outcomes, learning activities and assessments are constructively aligned. In doing so, the team will need to assess if
- Course outcomes are written clearly and in a measurable manner
- Course assessments aligned with course outcomes ; which assessment is aligned to which outcome, and if they are not aligned, should outcomes or assessments be removed/modified? (note one assessment may evaluate multiple outcomes)
- the content provided adequately prepares students to achieve expectations set in course outcomes and the learning activities provide opportunities for students to practice/apply knowledge, skills and competencies that we are preparing for them to be measured on.

