Labs and Activities
Week 3 – the Nervous System
Learning Objectives
Upon completing this learning package, the student will be expected to recall the following.
Click the triangle drop-down to see specific objectives:
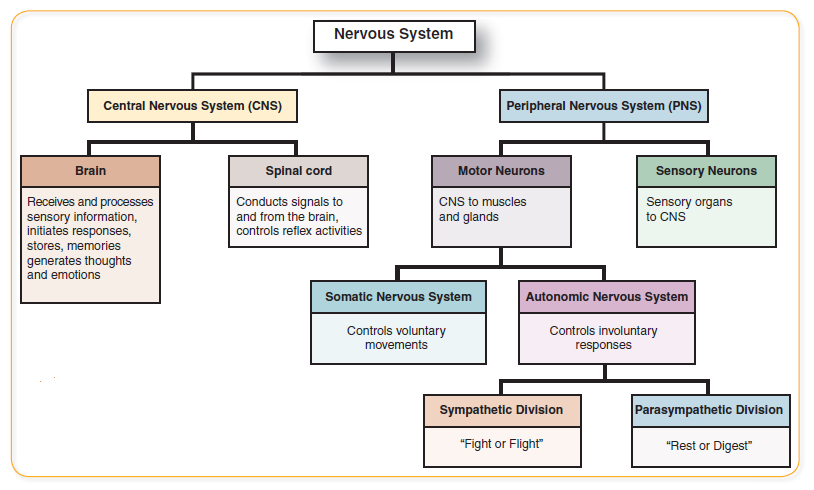
Divisions of the Nervous System
- Define the following two main subdivisions of the nervous system:
- Central nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
- Using the diagram provided, identify the basic organizational divisions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
- State the general function(s) of the following divisions of the nervous system: (use Figure 3.1 Organization of the Nervous System below as an outline).
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Afferent (sensory) system
- Efferent (motor) system
- Somatic system (somatic sensory and somatic motor)
- Autonomic system (autonomic sensory and autonomic motor)
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- Enteric nervous system (enteric plexuses)
Description of Nerve Tissue
- State a definition and its general function(s) in the nervous system
- Neuron
- Neuroglia
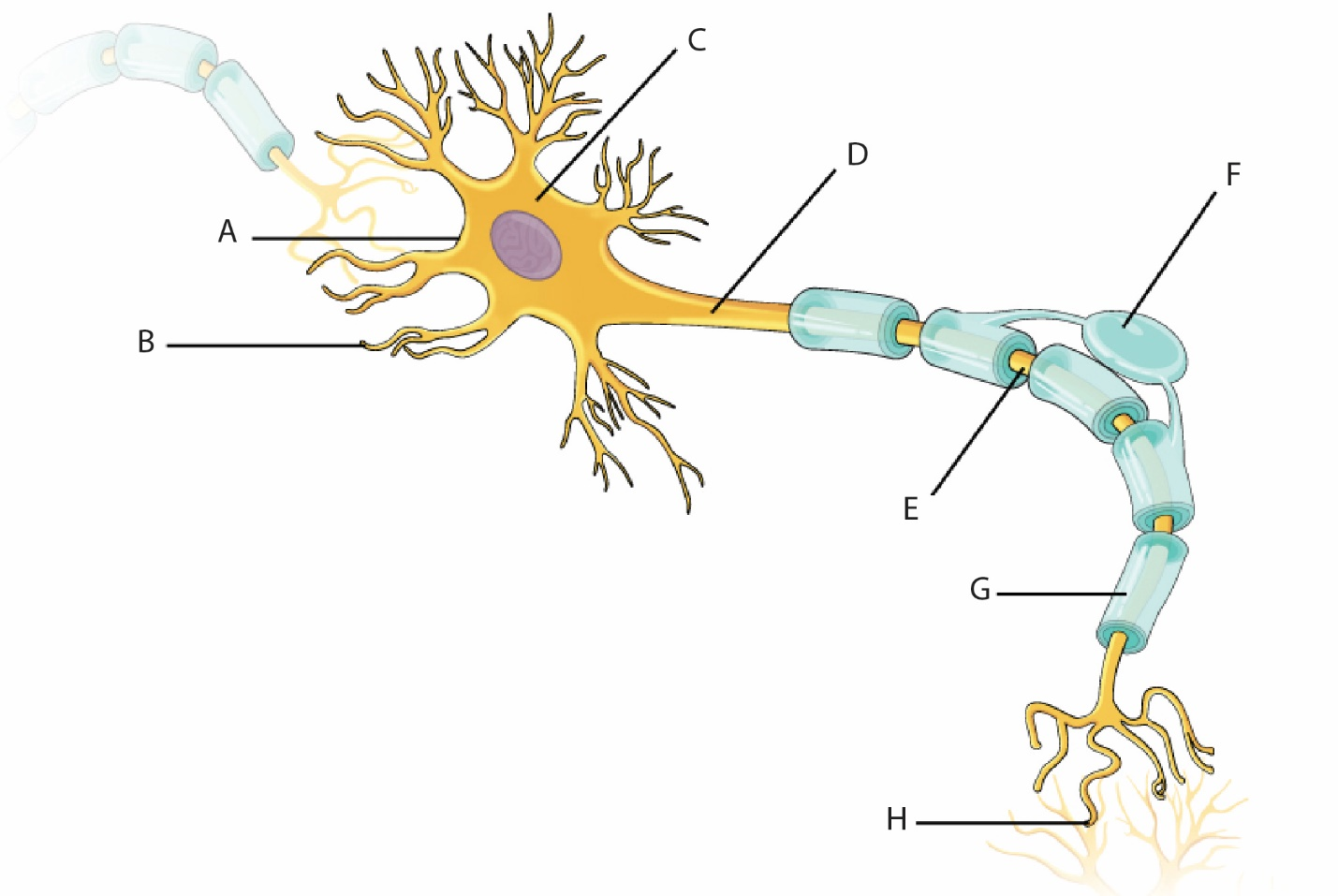
- Define, locate in a diagram, and identify the function of each of the following parts of a multipolar neuron and associated structures: (Use The Neuron Structural Components Diagram)
- Cell body
- Nerve fibres
- Dendrite
- Axon (axon collaterals)
- Synaptic end bulb and synaptic vesicle
- Myelin sheath
- Schwann cell
- Neurolemma
- Distinguish between a multipolar neuron, a bipolar neuron and a unipolar neuron. (based on structural classification of neurons)
- State the function of the following types of neurons: (based on a functional classification of neurons)
- Sensory (usually are unipolar or bipolar neurons)
- Motor (usually are multipolar neurons)
- Interneuron (association neuron) (usually are multipolar neurons)
Structural Components of the Nervous System
- Define each of the following terms that are components of the nervous system:
- Sensory receptor
- Effector
- Gray matter of the spinal cord
- White matter of the spinal cord
- Tract (sensory and motor) of the spinal cord
- Nerves (sensory, motor and mixed)
- Ganglia of PNS or nuclei of CNS
- Reflex arc
- State a definition and their location and function in the three neuron reflex arc, for each component (See Figure 3.2 The Reflex Arc)
- Sensory receptor
- Sensory neuron (location in spinal nerve, posterior root ganglion and posterior root)
- Interneuron (location in spinal cord)
- Motor neuron (location in spinal cord, anterior root and spinal nerve)
- Synapses
- Neuroeffector junction
- Effector
- Describe in writing the pathway that a nerve impulse follows from sensory receptor in the (3 neuron) reflex arc to effector. Clearly state the location of the dendrite, cell body and axon for each neuron in the pathway (See Figure 3.2 below).
Central Nervous System (Introduction to the Spinal Cord)
- Identify, for the spinal cord:
- the body cavity where it is located
- the origin of the spinal cord
- the level of the vertebral column at which the spinal cord ends in early childhood and in the adult.
- gray matter and white matter
- tract (sensory and motor)
- State the two functions of the spinal cord as given below:
- the spinal cord functions as a two-way conduction pathway between the brain and spinal nerves
- the spinal cord is the control center for the spinal reflexes
- State the following information about spinal nerves:
- the names and numbers of the spinal nerves according to the level of the vertebral column from which they arise
- the name of the root in which sensory fibres of spinal nerves enter the spinal cord
- the name of the root from which motor fibres of spinal nerves leave the spinal cord
- Identify on a cross section of the spinal cord the components of a sensory fibre of a spinal nerve including location of sensory neuron.
- Identify on a cross section of the spinal cord the components of a motor fibre of a spinal nerve including the location of somatic and autonomic motor neurons.
- Describe the organization of spinal nerves into plexuses, according to the following guidelines:
- definition of term neural plexus
- name of main spinal nerve branch from which plexuses are formed
- name of four main plexuses out of which nerves emerge to run to somatic effectors
- Identify the plexus from which the following spinal nerves arise and the somatic effector(s) receiving its impulses through the nerve
- phrenic
- radial
- femoral
- sciatic
Lab Part 1: Reflex Arc and Types of Neurons
The purpose of these activities are to understand the three basic types of neurons found in a reflex arc, to locate the parts of a reflex arc on a model of the spinal cord
Materials Required:
- Part 1A
- Activity Kit titled “Types of Neurons” which contains:
- a schematic representation of a cross-section of the spinal cord
- 3 strings. Each string consists of 2 pieces of yarn of different colours with a button attached. Each string represents a neuron.
- Activity Kit titled “Types of Neurons” which contains:
- Part 1B
- Model of the spinal cord in the fifth cervical vertebra
- Part 1C
- Percussion Hammer
Part 1A: Types of Neurons
- The blue portion of the string (neuron) represents the dendrite.
- The yellow portion of the string (neuron) represents the axon.
- The button represents the cell body.
Question: What are the three types of neurons?
- Identify the type of neuron represented by each string. (Hint: for each neuron compare their relative lengths and whether they are unipolar or multipolar).
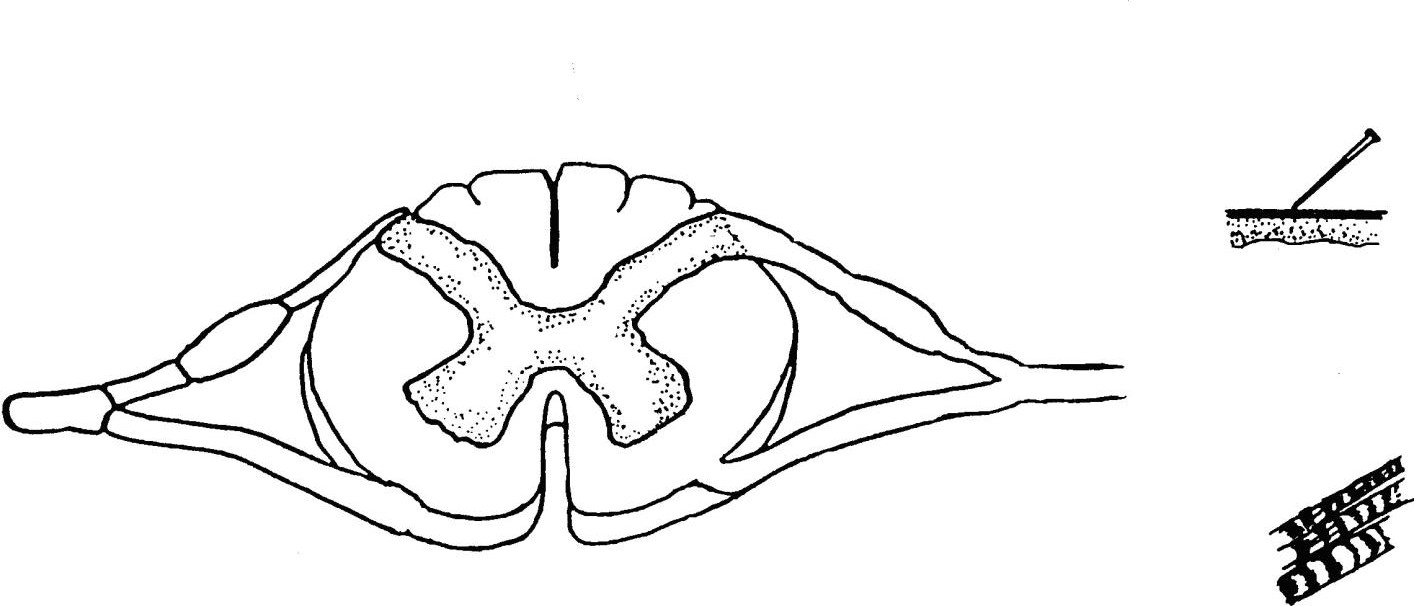
- Trace a simple 3 neuron reflex arc through the diagram by placing the neurons in the appropriate order, progressing from receptor to effector. As you go, state out loud the parts of the reflex arc including the types of neurons and the parts of each neuron.
- On the diagram below (Fig. 2) draw the parts of a reflex arc.
Download and label the following figure by right-clicking on the image and choosing “Save Image As”.
Part 1B: Reflex Arc and the Spinal Cord
- Obtain the model of the cross section of the spinal cord.
- Locate the following components of the reflex arc on this model:
- sensory neuron (location in spinal nerve, posterior root ganglion and posterior root)
- interneuron (location in spinal cord)
- motor neuron (location in spinal cord and anterior root)
- synapses
- neuroeffector junction
- Relative to this model, where would you find:
- The receptor
- The effector
- The neuroeffector junction
Part 1C: The Human Patellar Reflex
Reflex testing is used clinically by physicians in diagnosing suspected damage to the nerves, brain or spinal cord. Because reflex responses can be influenced by many factors other than disease or injury (e.g. emotional status, age, environmental circumstances, etc.), repeated tests on different occasions are usually employed.
- Perform this experiment in groups of 2 or 3.
- Seat the subject on the edge of the bench so that the legs hang freely and are relaxed and flexed at right angles to the thigh. Instruct the subject to keep her eyes closed unless otherwise indicated.
- Locate the patellar ligament just below the kneecap, and tap it with a percussion hammer, or with the edge of your hand.
- Test this reflex in both legs under the following conditions:
- Control (normal) test. Proceed as described in step 3.
- Have the subject perform a concentrated mental task such as adding a column of numbers, or counting backwards from 100 by 7s.
- Have the subject clench the fists of both hands tightly.
- Tap the patellar ligament of the right knee while the subject contracts the flexor muscles of the left thigh only. Compare responses of the two legs to each other, as well as to control.
- Allow the subject to watch the test being done.
- Grade reflexes as hyperactive, normal, diminished or absent in comparison with the first test.
Questions
- Using a diagram, describe the reflex pathway involved in this test. What is its normal function?
- Compare the effects of mental activity, and of increased muscle tension with the control, and explain.
- Predict the effects of each of the following on the patellar reflex. Consider both immediate and long-term results. Would voluntary knee action be affected?
- complete section of the spinal cord in the thoracic region.
- section of dorsal roots of the spinal nerves to the leg.
- section of ventral roots of the nerves to the leg.
Lab Part 2: Components of the Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
In this lab activity, you will identify the parts of the spinal cord and a reflex arc on a diagram, and then on a model of a vertebra.
Materials Required:
- Diagram of a cross-section of the spinal cord
- Model of the fifth cervical vertebra
Part 2A
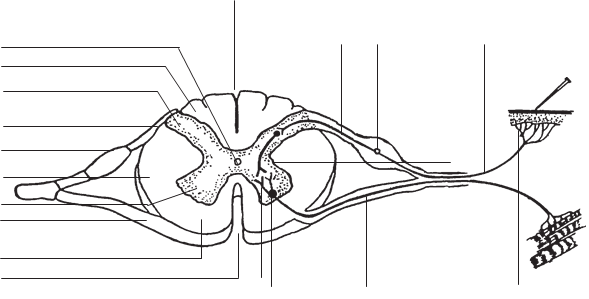
- Label the numbered components of the spinal cord and of the spinal nerves on Figure 3.4 Diagram of Spinal Cord. Download and label the figure by right-clicking on the image and choosing “Save Image As”.
- Anterior Median Fissure
- Posterior Median Sulcus
- Anterior Gray Horn
- Posterior Gray Horn
- Lateral Gray Horn
- Anterior White Column
- Lateral White Column
- Posterior White Column
- Central Canal
- Anterior Root
- Posterior Root
- Posterior Root Ganglion
- Dendrite of sensory fiber
- Cell body of sensory fiber
- Axon of sensory fiber
- Dendrite of motor fiber
- Cell body of motor fiber
- Axon of motor fiber
Part 2B: Model of Vertebra
- Locate the parts of the reflex arc on the model.
- Locate the parts of the spinal cord on the model.
Lab Part 3: Spinal Nerves, Plexuses, and Effectors
Part 3A
For each of the following effector activities, identify:
- the nerve pathway
- plexus from which the nerve arises
- effector
| Effector Activity | Nerve Pathway | Plexus | Effector |
|---|---|---|---|
| (i) Extension of elbow/arm | |||
| (ii) Extension of hip | |||
| (iii) Extension of knee | |||
| (iv) Flexion of hip | |||
| (v) Flexion of knee |

