Labs and Activities
Week 1 Package 2 – The Kidney: Microscopic Structure
In this package, the student will study the microscopic structure of the kidney.
Combined with the knowledge of macroscopic structure and function, this information will serve as a basis for the understanding of kidney physiology.
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this learning package, the student will be expected to recall:
- Nephrons are the functional units of the kidney. Each kidney has approximately one million nephrons. Identify and describe the two parts of a nephron.
- renal corpuscle – which is designed to filter the blood
- renal tubule – which is designed to modify the contents of the filtrate after it leaves the Bowman’s capsule
- Define each of the following components of the renal corpuscle
- glomerulus
- Bowman’s capsule (glomerular capsule)
- Locate the following components of the renal tubule and associated ducts
- proximal convoluted tubule
- loop of Henle (descending limb and ascending limb)
- distal convoluted tubule
- collecting duct
- papillary duct
- Outline the path the filtrate follows from the Bowman’s capsule cavity until it leaves the papillary ducts.
- Outline the pathway that blood flows through from its point of entry into the kidney to its point of exit
- renal artery, segmental artery, interlobar artery, arcuate artery
- cortical radiate artery
- afferent arteriole
- glomerulus
- efferent arteriole
- peritubular capillaries
- venules
- cortical radiate vein, arcuate veins, interlobar veins, segmental vein, renal vein
- Describe a unique feature of the kidney’s vascular system
- the names and type of vessel entering and exiting the glomerulus
- the functional significance of these vessels
- the specific location of the two capillary beds which the blood flows through
- Describe the wall of the renal tubule
- type of tissue which makes up the wall of the renal tubule
- similarities and difference in cell structure between the proximal convoluted tubule and the distal convoluted tubule
- Describe the juxtaglomerular apparatus
- location and overall purpose as part of the nephron structure
- define/describe macula densa
- define/describe juxtaglomerular cells
- name the enzyme secreted by the juxtaglomerular cells
- Describe the enzyme renin
- the stimulus for its release
- the action of this ENZYME
- ultimate effect on blood pressure once renin has been released
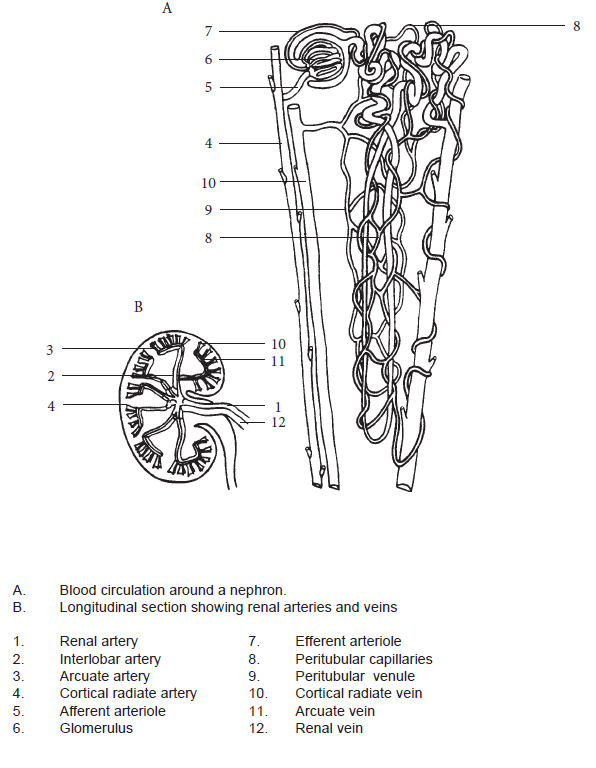
Test your knowledge of the blood vessels supplying the nephron unit by labelling Figure 1.2.1 Blood Vessels Supplying the Nephron Unit (provided in Part A), and by pointing at the structures in a dissected pig kidney.
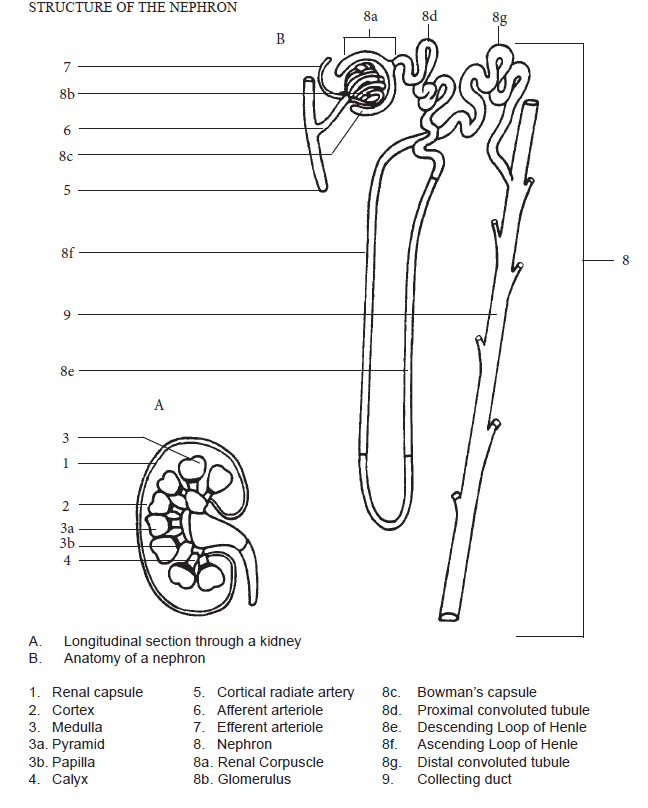
Test your knowledge of the structures composing the nephron unit by labelling Figure 1.2.2 Structure of the Nephron (provided in Part B) and by studying the cross section of medulla and cortex.
Lab Activities
Part A – Nephron: Blood
- Identify the following blood vessels supplying the nephron unit from Figure 1.2.1 Blood Vessels Supplying the Nephron Unit:
- Renal artery
- Cortical radiate artery
- Afferent arteriole
- Glomerulus
- Efferent arteriole
- Peritubular capillaries
- Venules
- Cortical radiate vein
- Renal vein
- Download and label the figure by right-clicking on the image and choosing “Save Image As”.
Part B – Nephron: Structure
- Identify the following five structures composing the nephron unit from Figure 1.2.2 Structure of the Nephron:
- Glomerulus
- Bowman’s capsule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Locate these nephron components (where possible) on the c.s. and l.s. of kidney, medulla and cortex.
- Download and label the figure by right-clicking on the image and choosing “Save Image As”.