Labs and Activities
Week 10 – Male Reproductive System
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this learning package, the student will be expected to recall the following.
Click the triangle drop-down to see specific objectives.
- Define each of the following components of the renal corpuscle
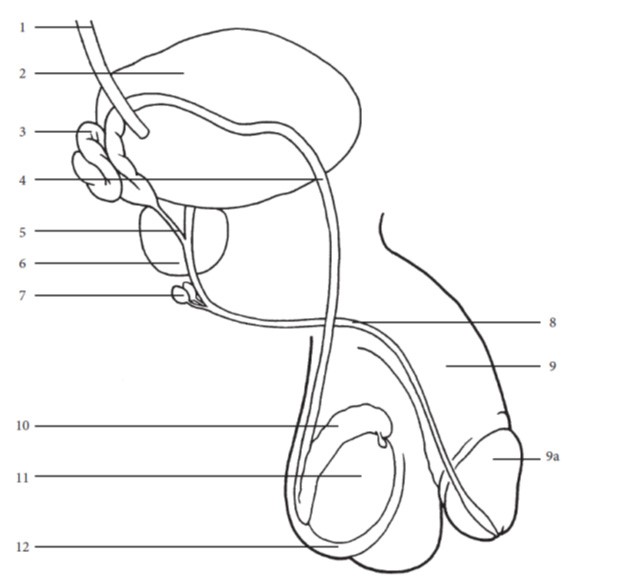
- Identify each of the following components of the male reproductive system on the diagrams in Appendix I and the models in the lab:
- ureter
- bladder
- seminal vesicle
- vas deferens
- ejaculatory duct
- prostate gland
- bulbourethral gland (Cowper’s gland)
- urethra
- penis
- glans
- epididymis
- testis (plural: testes)
- scrotum
- corpus cavernosum (plural: corpora cavernosa)
- corpus spongiosum
- spermatic cord
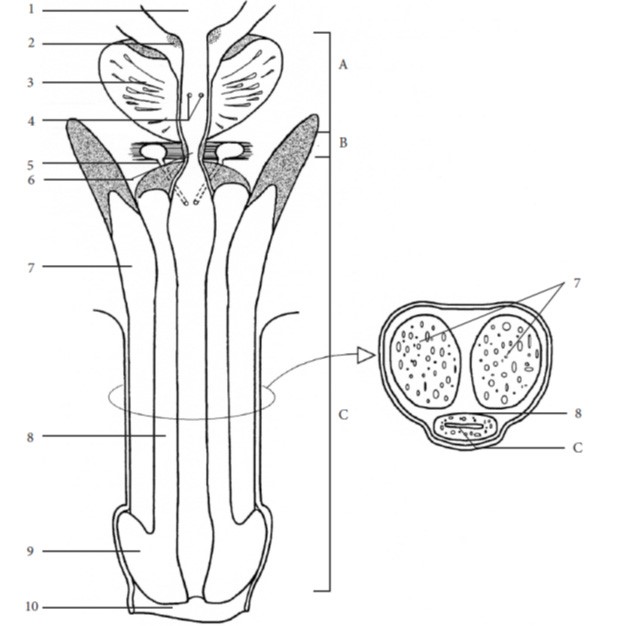
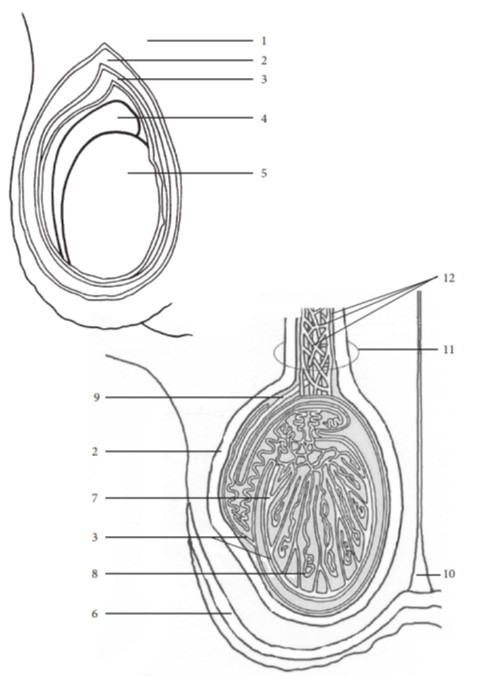
- Describe the male gonads, the testes, considering:
- location in the adult
- number
- c) function of seminiferous tubules
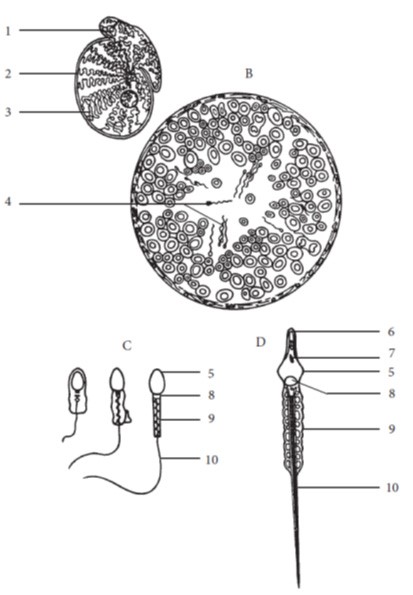
- State, for the male gamete, the sperm:
- the structural and functional features of the head, mid portion, and tail
- the hormone responsible for their development and maturation
- average number per ml. of ejaculate
- average life expectancy within the female reproductive tract
- State the location, tissues (and their functions) making up the wall of these structures, and functions in relation to maturation, storage and/or distribution of sperm for each of the following portions of the pathway for sperm:
- epididymis
- vas deferens
- ejaculatory duct
- urethra (prostatic, intermediate (membranous) and spongy divisions)
- State the components, in order, through which the male sex cells pass from their site of formation to their exit from the male reproductive system.
- State the effects of testosterone secretion on each of the following:
- male sex organs
- musculoskeletal system
- fluid and electrolyte balance
- sex drive/libido
- anterior pituitary gland hormonal secretion
- State the location, numbers, components of the secretion and their function(s), point of entry of secretion into the reproductive pathway, and contribution of secretion to male fertility for each of the following accessory reproductive organs:
- seminal vesicle
- bulbourethral gland (Cowper’s gland)
- prostate gland
- State the location, macroscopic component(s) of the male reproductive system contained within each, function(s) in relation to support, protection, sperm distribution and/or elimination from the male for each of the following support structures of the male reproductive organs:
- scrotum
- spermatic cords
- penis
Puberty
- Describe the physiological changes indicating the onset of sexual maturity in males, according to the following guidelines:
- approximate age range and developmental stage at which puberty begins in the male
- two hormonal stimuli and their source which initiate the onset of male puberty
- primary action of each hormone on the male sex gonads
- four physical signs of sexual maturation
- hormone and its source which is responsible for the development of the male secondary sex characteristics
- State the functions of each of the following hormones on the post pubescent male:
- S.H.
- H. (I.C.S.H.)
- Testosterone
- Describe the male secretion, semen, according to the following guidelines:
- three types of constituents and their sources
- pH
- average volume per ejaculation
- average number of sex cells per ejaculation
- role of each constituent in male/female fertility
- Define each of the following sexual/reproductive processes involved in elimination of semen from the system:
- erection
- emission
- ejaculation
- State the division(s) of the autonomic nervous system responsible for the male:
- erection
- emission
- ejaculation
- Identify the components, in order, of each of the following pathways of semen:
- from the testes to the exit from the male
- from the testes to the site of union with the female ovum
Lab Activity
Male Reproductive System
Download and label the following figures by right-clicking on the image and choosing “Save Image As”.